IL-1β, IL-6 promoter, TNF-α promoter and IL-1RA gene polymorphisms and the risk of preterm delivery due to preterm premature rupture of membranes in a population of Polish women
- PMID: 22371799
- PMCID: PMC3284070
- DOI: 10.5114/aoms.2010.14467
IL-1β, IL-6 promoter, TNF-α promoter and IL-1RA gene polymorphisms and the risk of preterm delivery due to preterm premature rupture of membranes in a population of Polish women
Abstract
Introduction: Our previous study revealed that anti-inflammatory cytokine gene polymorphisms increase the risk of spontaneous preterm delivery (PD) in a population of Polish women. Different genetic background of PD due to preterm premature rupture of membranes (pPROM) than PD without pPROM has been suggested. The aim of this study was to examine the relationship between the maternal carriage of polymorphic alleles of the following genes: interleukin 1β(IL-1β [+3953C>T]), interleukin 6 promoter (IL-6 [-174G>C]), tumour necrosis factor promoter (TNF-α [-308G>A]) and interleukin 1 receptor antagonist (IL-1RN) and the risk of PD caused exclusively by pPROM in a population of Polish women.
Material and methods: A case-control study. 95 Caucasian women were examined including 32 cases and 63 controls. Case subjects experienced a delivery at less than 36 weeks and 6 days of gestation due exclusively to pPROM while control subjects gave birth at term. Polymorphisms were determined by polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis (PCR-RFLP).
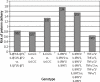
Results: NO STATISTICALLY SIGNIFICANT RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN POLYMORPHISMS OF EXAMINED GENES AND RISK OF PD DUE TO PPROM IN A POPULATION OF POLISH WOMEN WAS FOUND: OR = 0.84 (95% CI: 0.34-2.01) for IL-1β, OR = 0.77 (95% CI: 0.27-2.13) for IL-6, OR = 0.72 (95% CI: 0.26-1.90) for TNF-α and OR = 1.74 (95% CI: 0.66-4.64) for IL-1RN.
Conclusions: Maternal carriage of polymorphic alleles of IL-1β, IL-6 promoter, TNF-α promoter and IL-1RA seems to have no impact on the risk of PD due to pPROM in the population of Polish women.The genetic contribution and pathomechanism of PD related to pPROM seems to differ from those of spontaneous PD without pPROM.
Keywords: cytokines; genetic polymorphism; pathomechanism; prematurity.
Figures
References
-
- Parry S, Strauss JF., 3rd Premature rupture of the fetal membranes. N Engl J Med. 1998;338:663–70. - PubMed
-
- Sebire NJ. Choriodecidual inflammatory syndrome (CoDIS) is the leading, and under recognised, cause of early preterm delivery and second trimester miscarriage. Med Hypotheses. 2001;56:497–500. - PubMed
-
- Genç MR, Gerber S, Nesin M, Witkin SS. Polymorphism in the interleukin-1 gene complex and spontaneous preterm delivery. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2002;187:157–63. - PubMed
-
- Simhan HN, Krohn MA, Roberts JM, Zeevi A, Caritis SN. Interleukin-6 promoter –174 polymorphism and spontaneous preterm birth. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2003;189:915–8. - PubMed
-
- Kent AS, Sullivan MH, Sun MY, Zosmer A, Elder MG. Effects of interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha on prostaglandin production by cultured human fetal membranes. Prostaglandins. 1993;46:351–9. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials