DeviceEditor visual biological CAD canvas
- PMID: 22373390
- PMCID: PMC3317443
- DOI: 10.1186/1754-1611-6-1
DeviceEditor visual biological CAD canvas
Abstract
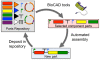
Background: Biological Computer Aided Design (bioCAD) assists the de novo design and selection of existing genetic components to achieve a desired biological activity, as part of an integrated design-build-test cycle. To meet the emerging needs of Synthetic Biology, bioCAD tools must address the increasing prevalence of combinatorial library design, design rule specification, and scar-less multi-part DNA assembly.
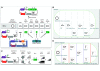
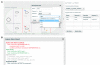
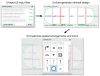
Results: We report the development and deployment of web-based bioCAD software, DeviceEditor, which provides a graphical design environment that mimics the intuitive visual whiteboard design process practiced in biological laboratories. The key innovations of DeviceEditor include visual combinatorial library design, direct integration with scar-less multi-part DNA assembly design automation, and a graphical user interface for the creation and modification of design specification rules. We demonstrate how biological designs are rendered on the DeviceEditor canvas, and we present effective visualizations of genetic component ordering and combinatorial variations within complex designs.
Conclusions: DeviceEditor liberates researchers from DNA base-pair manipulation, and enables users to create successful prototypes using standardized, functional, and visual abstractions. Open and documented software interfaces support further integration of DeviceEditor with other bioCAD tools and software platforms. DeviceEditor saves researcher time and institutional resources through correct-by-construction design, the automation of tedious tasks, design reuse, and the minimization of DNA assembly costs.
Figures




References
-
- Chandran D, Bergmann FT, Sauro HM, Densmore D. In: Design and Analysis of Bio-molecular Circuits. 1. Koeppl H, Densmore D, di Bernardo M, Setti G, editor. New York, Springer-Verlag; 2011. Computer-aided design for synthetic biology; pp. 203–224.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

