Disruption of NMDAR-CRMP-2 signaling protects against focal cerebral ischemic damage in the rat middle cerebral artery occlusion model
- PMID: 22373559
- PMCID: PMC3367672
- DOI: 10.4161/chan.18919
Disruption of NMDAR-CRMP-2 signaling protects against focal cerebral ischemic damage in the rat middle cerebral artery occlusion model
Abstract
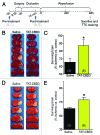
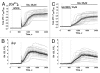
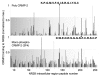
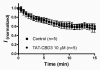
Collapsin response mediator protein 2 (CRMP-2), traditionally viewed as an axon/dendrite specification and axonal growth protein, has emerged as nidus in regulation of both pre- and post-synaptic Ca ( 2+) channels. Building on our discovery of the interaction and regulation of Ca ( 2+) channels by CRMP-2, we recently identified a short sequence in CRMP-2 which, when appended to the transduction domain of HIV TAT protein, suppressed acute, inflammatory and neuropathic pain in vivo by functionally uncoupling CRMP-2 from the Ca ( 2+) channel. Remarkably, we also found that this region attenuated Ca ( 2+) influx via N-methylD-Aspartate receptors (NMDARs) and reduced neuronal death in a moderate controlled cortical impact model of traumatic brain injury (TBI). Here, we sought to extend these findings by examining additional neuroprotective effects of this peptide (TAT-CBD3) and exploring the biochemical mechanisms by which TAT-CBD3 targets NMDARs. We observed that an intraperitoneal injection of TAT-CBD3 peptide significantly reduced infarct volume in an animal model of focal cerebral ischemia. Neuroprotection was observed when TAT-CBD3 peptide was given either prior to or after occlusion but just prior to reperfusion. Surprisingly, a direct biochemical complex was not resolvable between the NMDAR subunit NR2B and CRMP-2. Intracellular application of TAT-CBD3 failed to inhibit NMDAR current. NR2B interactions with the post synaptic density protein 95 (PSD-95) remained intact and were not disrupted by TAT-CBD3. Peptide tiling of intracellular regions of NR2B revealed two 15-mer sequences, in the carboxyl-terminus of NR2B, that may confer binding between NR2B and CRMP-2 which supports CRMP-2's role in excitotoxicity and neuroprotection.
Keywords: CRMP-2; MCAO model; N-methylD-aspartate receptor; focal cerebral ischemia; peptide.
Figures
Comment on
- Brittain JM, Chen L, Wilson SM, Brustovetsky T, Gao X, Ashpole NM, et al. Neuroprotection against traumatic brain injury by a peptide derived from the collapsin response mediator protein 2 (CRMP-2) J Biol Chem. 2011;286:37778–92. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.255455. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.255455
References
-
- Benveniste H, Drejer J, Schousboe A, Diemer NH. Elevation of the extracellular concentrations of glutamate and aspartate in rat hippocampus during transient cerebral ischemia monitored by intracerebral microdialysis. J Neurochem. 1984;43:1369–74. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1984.tb05396.x. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
