Defining signal transduction by inositol phosphates
- PMID: 22374098
- PMCID: PMC3925325
- DOI: 10.1007/978-94-007-3015-1_13
Defining signal transduction by inositol phosphates
Abstract
Ins(1,4,5)P(3) is a classical intracellular messenger: stimulus-dependent changes in its levels elicits biological effects through its release of intracellular Ca(2+) stores. The Ins(1,4,5)P(3) response is "switched off" by its metabolism to a range of additional inositol phosphates. These metabolites have themselves come to be collectively described as a signaling "family". The validity of that latter definition is critically examined in this review. That is, we assess the strength of the hypothesis that Ins(1,4,5)P(3) metabolites are themselves "classical" signals. Put another way, what is the evidence that the biological function of a particular inositol phosphate depends upon stimulus dependent changes in its levels? In this assessment, examples of an inositol phosphate acting as a cofactor (i.e. its function is not stimulus-dependent) do not satisfy our signaling criteria. We conclude that Ins(3,4,5,6)P(4) is, to date, the only Ins(1,4,5)P(3) metabolite that has been validated to act as a second messenger.
Figures
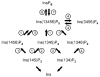
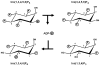
References
-
- Alcázar-Román AR, Tran EJ, Guo S, Wente SR. Inositol hexakisphosphate and Gle1 activate the DEAD-box protein Dbp5 for nuclear mRNA export. Nat Cell Biol. 2006;8:645–647. - PubMed
-
- Ali N, Craxton A, Shears SB. Hepatic Ins(1,3,4,5)P4 3-phosphatase is compartmentalized inside endoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1993;268:6161–6167. - PubMed
-
- Balla T, Guillemette G, Baukal AJ, Catt KJ. Formation of inositol 1,3,4,6-tetrakisphosphate during angiotensin II action in bovine adrenal glomerulosa cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987;146:199–205. - PubMed
-
- Barg S, Huang P, Eliasson L, Nelson DJ, Obermüller S, Rorsman P, Thévenod F, Renström E. Priming of insulin granules for exocytosis by granular chloride uptake and acidification. J Cell Sci. 2001;114:2145–2154. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

