MiR-205 determines the radioresistance of human nasopharyngeal carcinoma by directly targeting PTEN
- PMID: 22374676
- PMCID: PMC3356830
- DOI: 10.4161/cc.11.4.19228
MiR-205 determines the radioresistance of human nasopharyngeal carcinoma by directly targeting PTEN
Abstract
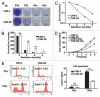
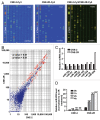
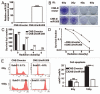
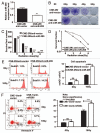
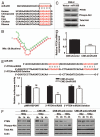
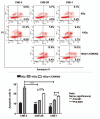
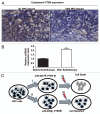
Radiotherapy is the primary treatment for nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC), but radioresistance severely reduces NPC radiocurability. Here, we have established a radio-resistant NPC cell line, CNE-2R, and investigate the role of miRNAs in radioresistance. The miRNAs microarray assay reveals that miRNAs are differentially expressed between CNE-2R and its parental cell line CNE-2. We find that miR-205 is elevated in CNE-2R. A target prediction algorithm suggests that miR‑205 regulates expression of PTEN, a tumor-suppressor. Introducing miR-205 into CNE-2 cells suppresses PTEN protein expression, followed by activation of AKT, increased number of foci formation and reduction of cell apoptosis postirradiation. On the other hand, knocking down miR-205 in CNE-2R cells compromises the inhibition of PTEN and increases cell apoptosis. Significantly, immunohistochemistry studies demonstrate that PTEN is downregulated at late stages of NPC, and that miR-205 is significantly elevated followed the radiotherapy. Our data conclude that miR-205 contributes to radioresistance of NPC by directly targeting PTEN. Both miR-205 and PTEN are potential predictive biomarkers for radiosensitivity of NPC and may serve as targets for achieve successful radiotherapy in NPC.
Figures
References
-
- Chang JT, Ko JY, Hong RL. Recent advances in the treatment of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J Formos Med Assoc. 2004;103:496–510. - PubMed
-
- Mostafa E, Nasar MN, Rabie NA, Ibrahim SA, Barakat HM, Rabie AN. Induction chemotherapy with paclitaxel and cisplatin, followed by concomitant cisplatin and radiotherapy for the treatment of locally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J Egypt Natl Canc Inst. 2006;18:348–356. - PubMed
-
- Gupta AK, McKenna WG, Weber CN, Feldman MD, Goldsmith JD, Mick R, et al. Local recurrence in head and neck cancer: relationship to radiation resistance and signal transduction. Clin Cancer Res. 2002;8:885–892. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
