Rapamycin inhibition of baculovirus recombinant (BVr) ribosomal protein S6 kinase (S6K1) is mediated by an event other than phosphorylation
- PMID: 22376175
- PMCID: PMC3311567
- DOI: 10.1186/1478-811X-10-4
Rapamycin inhibition of baculovirus recombinant (BVr) ribosomal protein S6 kinase (S6K1) is mediated by an event other than phosphorylation
Abstract
Background: Ribosomal protein S6 kinase 1(S6K1) is an evolutionary conserved kinase that is activated in response to growth factors and viral stimuli to influence cellular growth and proliferation. This downstream effector of target of rapamycin (TOR) signaling cascade is known to be directly activated by TOR- kinase mediated hydrophobic motif (HM) phosphorylation at Threonine 412 (T412). Selective loss of this phosphorylation by inactivation of TOR kinase or activation/recruitment of a phosphatase has accordingly been implicated in mediating inhibition by rapamycin.
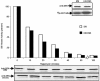
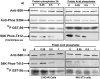
Findings: We present evidence that baculovirus driven expression of S6K1 in insect cells (Sf9) fails to activate the enzyme and instead renders it modestly active representing 4-6 folds less activity than its fully active mammalian counterpart. Contrary to the contention that viral infection activates TOR signaling pathway, we report that BVr enzyme fails to exhibit putative TOR dependent phosphorylation at the HM and the resultant phosphorylation at the activation loop (AL) of the enzyme, correlating with the level of activity observed. Surprisingly, the BVr enzyme continued to exhibit sensitivity to rapamycin that remained unaffected by mutations compromised for TOR phosphorylation (T412A) or deletions compromised for TOR binding (ΔNH 2-46/ΔCT104).
Conclusions: These data together with the ability of the BVr enzyme to resist inactivation by phosphatases indicate that inhibition by rapamycin is not mediated by any phosphorylation event in general and TOR dependent phosphorylation in particular.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Loss of hydrophobic motif and activation loop phosphorylation is a consequence and not the mechanism of S6 kinase 1 inhibition by rapamycin.J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2013 Apr-Jun;27(2):399-408. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2013. PMID: 23830390
-
Hydrophobic motif phosphorylation is not required for activation loop phosphorylation of p70 ribosomal protein S6 kinase 1 (S6K1).J Biol Chem. 2011 Jul 1;286(26):23552-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.258004. Epub 2011 May 11. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21561857 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of a conserved C-terminal motif (RSPRR) in ribosomal protein S6 kinase 1 required for its mammalian target of rapamycin-dependent regulation.J Biol Chem. 2005 Mar 25;280(12):11101-6. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M413995200. Epub 2005 Jan 19. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 15659381
-
Regulation of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, Akt/protein kinase B, FRAP/mammalian target of rapamycin, and ribosomal S6 kinase 1 signaling pathways by thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) and stimulating type TSH receptor antibodies in the thyroid gland.J Biol Chem. 2003 Jun 13;278(24):21960-71. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M300805200. Epub 2003 Mar 30. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12668683
-
Serotonin-induced growth of pulmonary artery smooth muscle requires activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/serine-threonine protein kinase B/mammalian target of rapamycin/p70 ribosomal S6 kinase 1.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2006 Feb;34(2):182-91. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2005-0163OC. Epub 2005 Sep 29. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2006. PMID: 16195541 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
mTOR Signaling in Protein Translation Regulation: Implications in Cancer Genesis and Therapeutic Interventions.Mol Biol Int. 2014;2014:686984. doi: 10.1155/2014/686984. Epub 2014 Nov 20. Mol Biol Int. 2014. PMID: 25505994 Free PMC article. Review.
-
mTORC1 induces eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E interaction with TOS-S6 kinase 1 and its activation.Cell Cycle. 2021 May;20(9):839-854. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2021.1901038. Epub 2021 May 3. Cell Cycle. 2021. PMID: 33938392 Free PMC article.
-
Growth inhibition by bupivacaine is associated with inactivation of ribosomal protein S6 kinase 1.Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:831845. doi: 10.1155/2014/831845. Epub 2014 Jan 29. Biomed Res Int. 2014. PMID: 24605337 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of a brief high-fat diet and acute exercise on the mTORC1 and IKK/NF-κB pathways in rat skeletal muscle.Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2015 Mar;40(3):251-62. doi: 10.1139/apnm-2014-0412. Epub 2014 Nov 17. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2015. PMID: 25706655 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of glucose availability on αS1-casein synthesis in bovine mammary epithelial cells.J Anim Sci. 2022 Nov 1;100(11):skac330. doi: 10.1093/jas/skac330. J Anim Sci. 2022. PMID: 36222748 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mukhopadhyay NK, Price DJ, Kyriakis JM, Pelech S, Sanghera J, Avruch J. An array of insulin-activated, proline-directed serine/threonine protein kinases phosphorylate the p70 S6 kinase. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:3325–3335. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

