Nonpasteurized dairy products, disease outbreaks, and state laws-United States, 1993-2006
- PMID: 22377202
- PMCID: PMC3309640
- DOI: 10.3201/eid1803.111370
Nonpasteurized dairy products, disease outbreaks, and state laws-United States, 1993-2006
Abstract
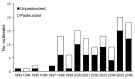
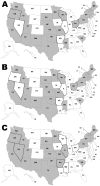
Although pasteurization eliminates pathogens and consumption of nonpasteurized dairy products is uncommon, dairy-associated disease outbreaks continue to occur. To determine the association of outbreaks caused by nonpasteurized dairy products with state laws regarding sale of these products, we reviewed dairy-associated outbreaks during 1993-2006. We found 121 outbreaks for which the product's pasteurization status was known; among these, 73 (60%) involved nonpasteurized products and resulted in 1,571 cases, 202 hospitalizations, and 2 deaths. A total of 55 (75%) outbreaks occurred in 21 states that permitted sale of nonpasteurized products; incidence of nonpasteurized product-associated outbreaks was higher in these states. Nonpasteurized products caused a disproportionate number (≈150× greater/unit of product consumed) of outbreaks and outbreak-associated illnesses and also disproportionately affected persons <20 years of age. States that restricted sale of nonpasteurized products had fewer outbreaks and illnesses; stronger restrictions and enforcement should be considered.
Figures
References
-
- US Department of Agriculture and US Department of Health and Human Services. Dietary guidelines for Americans, 2010. 7th ed. Washington: US Government Printing Office; 2010. - PubMed
-
- US Food and Drug Administration. FDA plans to ban raw milk. In: FDA consumer. Washington: US Government Printing Office; 1987.
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Outbreak of multidrug-resistant Salmonella enterica serotype Newport infections associated with consumption of unpasteurized Mexican-style aged cheese—Illinois, March 2006–April 2007. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2008;57:432–5. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
