Sidedness of interfacial arginine residues and anti-atherogenicity of apolipoprotein A-I mimetic peptides
- PMID: 22377531
- PMCID: PMC3329384
- DOI: 10.1194/jlr.M019844
Sidedness of interfacial arginine residues and anti-atherogenicity of apolipoprotein A-I mimetic peptides
Abstract
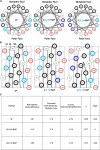
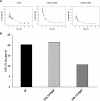
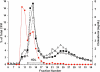
To test the hypothesis that sidedness of interfacial arginine (Arg) in apoA-I mimetic peptides, similar to that observed in apoA-I (Bashtovyy, D. et al. 2011. Sequence conservation of apolipoprotein A-I affords novel insights into HDL structure-function. J. Lipid Res. 52: 435-450.), may be important for biological activity, we compared properties of 4F and analogs, [K⁴,¹⁵>R]4F and [K⁹,¹³>R]4F, with Lys>Arg substitutions on the right and left side, respectively, of the 4F amphipathic helix. Intraperitoneal administration of these peptides into female apoE null mice (n = 13 in each group) reduced en face lesions significantly compared with controls; 4F and [K⁴,¹⁵>R]4F were equally effective whereas [K⁹,¹³>R]4F was less effective. Turnover experiments indicated that [K⁴,¹⁵>R]4F reached the highest, whereas [K⁹,¹³>R]4F had the lowest, plasma peak levels with a similar half life as the [K⁴,¹⁵>R]4F analog. The half life of 4F was two times longer than the other two peptides. The order in their abilities to associate with HDL in human plasma, generation of apoA-I particles with pre-β mobility from isolated HDL, lipid associating ability, and sensitivity of lipid complexes to trypsin digestion was: 4F>[K⁴,¹⁵,>R]4F>[K⁹,¹³>R]4F. These studies support our hypothesis that the sidedness of interfacial Arg residues in the polar face of apoA-I mimetics results in differential biological properties.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Apolipoprotein E mimetic is more effective than apolipoprotein A-I mimetic in reducing lesion formation in older female apo E null mice.Atherosclerosis. 2012 Oct;224(2):326-31. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2012.05.040. Epub 2012 Jun 23. Atherosclerosis. 2012. PMID: 22771190 Free PMC article.
-
Preservation of biological function despite oxidative modification of the apolipoprotein A-I mimetic peptide 4F.J Lipid Res. 2012 Aug;53(8):1576-87. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M026278. Epub 2012 May 15. J Lipid Res. 2012. PMID: 22589558 Free PMC article.
-
Apolipoprotein A-I mimetic peptide helix number and helix linker influence potentially anti-atherogenic properties.J Lipid Res. 2008 Jun;49(6):1268-83. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M700552-JLR200. Epub 2008 Mar 5. J Lipid Res. 2008. PMID: 18323574 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic inflammation, intestine, and paraoxonase-1.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2014;824:83-8. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-07320-0_8. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2014. PMID: 25038995 Review.
-
Apolipoprotein A-I mimetic peptides: a potential new therapy for the prevention of atherosclerosis.Cardiol Rev. 2010 May-Jun;18(3):141-7. doi: 10.1097/CRD.0b013e3181c4b508. Cardiol Rev. 2010. PMID: 20395699 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecules that mimic apolipoprotein A-I: potential agents for treating atherosclerosis.J Med Chem. 2014 Mar 27;57(6):2169-96. doi: 10.1021/jm4005847. Epub 2013 Oct 29. J Med Chem. 2014. PMID: 24168751 Free PMC article. Review.
-
D4F alleviates macrophage-derived foam cell apoptosis by inhibiting CD36 expression and ER stress-CHOP pathway.J Lipid Res. 2015 Apr;56(4):836-47. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M055400. Epub 2015 Jan 29. J Lipid Res. 2015. PMID: 25635126 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid complex of apolipoprotein A-I mimetic peptide 4F is a novel platform for paraoxonase-1 binding and enhancing its activity and stability.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013 Jan 18;430(3):975-80. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.11.128. Epub 2012 Dec 19. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013. PMID: 23261466 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and Safety of High-Density Lipoprotein/Apolipoprotein A1 Replacement Therapy in Humans and Mice With Atherosclerosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021 Aug 2;8:700233. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.700233. eCollection 2021. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021. PMID: 34422927 Free PMC article.
-
L-4F inhibits lipopolysaccharide-mediated activation of primary human neutrophils.Inflammation. 2014 Oct;37(5):1401-12. doi: 10.1007/s10753-014-9864-7. Inflammation. 2014. PMID: 24647607 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Harel M., Aharoni A., Gaidukov L., Brumshtein B., Khersonsky O., Meged R., Dvir H., Ravelli R. B. G., McCarthy A., Toker L., et al. 2004. Structure and evolution of the serum paraoxonase family of detoxifying and anti-atherosclerotic enzymes. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 11: 412–419 - PubMed
-
- Lund-Katz S., Phillips M. C., Mishra V. K., Segrest J. P., Anantharamaiah G. M. 1995. Microenvironments of basic amino acids in amphipathic alpha-helices bound to phospholipid: 13C NMR studies using selectively labeled peptides. Biochemistry. 34: 9219–9226 - PubMed
-
- Mishra V. K., Anantharamaiah G. M., Segrest J. P., Palgunachari M. N., Chaddha M., Sham S. W. S., Krishna N. R. 2006. Association of a model class A (Apolipoprotein) amphipathic α-helical peptide with lipid. J. Biol. Chem. 281: 6511–6519 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

