Cell density-dependent reduction of dihydroceramide desaturase activity in neuroblastoma cells
- PMID: 22377532
- PMCID: PMC3329391
- DOI: 10.1194/jlr.M019075
Cell density-dependent reduction of dihydroceramide desaturase activity in neuroblastoma cells
Abstract
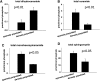
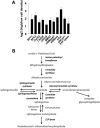
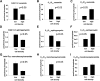
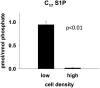
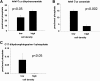
We applied a metabolic approach to investigate the role of sphingolipids in cell density-induced growth arrest in neuroblastoma cells. Our data revealed that sphingolipid metabolism in neuroblastoma cells significantly differs depending on the cells' population context. At high cell density, cells exhibited G0/G1 cell-cycle arrest and reduced ceramide, monohexosylceramide, and sphingomyelin, whereas dihydroceramide was significantly increased. In addition, our metabolic-labeling experiments showed that neuroblastoma cells at high cell density preferentially synthesized very long chain (VLC) sphingolipids and dramatically decreased synthesis of sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P). Moreover, densely populated neuroblastoma cells showed increased message levels of both anabolic and catabolic enzymes of the sphingolipid pathway. Notably, our metabolic-labeling experiments indicated reduced dihydroceramide desaturase activity at confluence, which was confirmed by direct measurement of dihydroceramide desaturase activity in situ and in vitro. Importantly, we could reduce dihydroceramide desaturase activity in low-density cells by applying conditional media from high-density cells, as well as by adding reducing agents, such as DTT and L-cysteine to the media. In conclusion, our data suggest a role of the sphingolipid pathway, dihydroceramides desaturase in particular, in confluence-induced growth arrest in neuroblastoma cells.
Figures
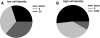
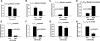


References
-
- Hannun Y. A., Obeid L. M. 2008. Principles of bioactive lipid signalling: lessons from sphingolipids. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 9: 139–150 - PubMed
-
- Nelson P. J., Daniel T. O. 2002. Emerging targets: molecular mechanisms of cell contact-mediated growth control. Kidney Int. 61: S99–S105 - PubMed
-
- Hall P. A., Lane D. P. 1994. Genetics of growth arrest and cell death: key determinants of tissue homeostasis. Eur. J. Cancer. 30A: 2001–2012 - PubMed
-
- Kopitz J., Muhl C., Ehemann V., Lehmann C., Cantz M. 1997. Effects of cell surface ganglioside sialidase inhibition on growth control and differentiation of human neuroblastoma cells. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 73: 1–9 - PubMed
-
- Rösner H., Greis C., Rodemann H. P. 1990. Density-dependent expression of ganglioside GM3 by human skin fibroblasts in an all-or-none fashion, as a possible modulator of cell growth in vitro. Exp. Cell Res. 190: 161–169 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

