Genotype-phenotype correlations in THAP1 dystonia: molecular foundations and description of new cases
- PMID: 22377579
- PMCID: PMC3358360
- DOI: 10.1016/j.parkreldis.2012.02.001
Genotype-phenotype correlations in THAP1 dystonia: molecular foundations and description of new cases
Abstract
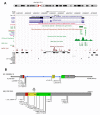
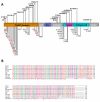
An extensive variety of THAP1 sequence variants have been associated with focal, segmental and generalized dystonia with age of onset ranging from 3 to over 60 years. In previous work, we screened 1114 subjects with mainly adult-onset primary dystonia (Neurology 2010; 74:229-238) and identified 6 missense mutations in THAP1. For this report, we screened 750 additional subjects for mutations in coding regions of THAP1 and interrogated all published descriptions of THAP1 phenotypes (gender, age of onset, anatomical distribution of dystonia, family history and site of onset) to explore the possibility of THAP1 genotype-phenotype correlations and facilitate a deeper understanding of THAP1 pathobiology. We identified 5 additional missense mutations in THAP1 (p.A7D, p.K16E, p.S21C, p.R29Q, and p.I80V). Three of these variants are associated with appendicular tremors, which were an isolated or presenting sign in some of the affected subjects. Abductor laryngeal dystonia and mild blepharospasm can be manifestations of THAP1 mutations in some individuals. Overall, mean age of onset for THAP1 dystonia is 16.8 years and the most common sites of onset are the arm and neck, and the most frequently affected anatomical site is the neck. In addition, over half of patients exhibit either cranial or laryngeal involvement. Protein truncating mutations and missense mutations within the THAP domain of THAP1 tend to manifest at an earlier age and exhibit more extensive anatomical distributions than mutations localized to other regions of THAP1.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Fuchs T, Gavarini S, Saunders-Pullman R, Raymond D, Ehrlich ME, Bressman SB, et al. Mutations in the THAP1 gene are responsible for DYT6 primary torsion dystonia. Nat Genet. 2009;41:286–8. - PubMed
-
- Ozelius LJ, Hewett JW, Page CE, Bressman SB, Kramer PL, Shalish C, et al. The early-onset torsion dystonia gene (DYT1) encodes an ATP-binding protein. Nat Genet. 1997;17:40–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P50-NS57567/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01NS069936/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 TR001456/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 NS072187-01S2/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 NS070276/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 NS065701/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- 1U54NS065701/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01NS048458/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS048458/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- 1RC2NS070276/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS057567/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS069936/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 NS072187/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

