Virion endocytosis is a major target for murid herpesvirus-4 neutralization
- PMID: 22377583
- PMCID: PMC3755512
- DOI: 10.1099/vir.0.040790-0
Virion endocytosis is a major target for murid herpesvirus-4 neutralization
Abstract
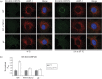
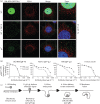
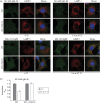
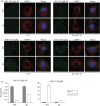
Herpesviruses consistently transmit from immunocompetent carriers, implying that their neutralization is hard to achieve. Murid herpesvirus-4 (MuHV-4) exploits host IgG Fc receptors to bypass blocks to cell binding, and pH-dependent protein conformation changes to unveil its fusion machinery only after endocytosis. Nevertheless, neutralization remains possible by targeting the virion glycoprotein H (gH)-gL heterodimer, and the neutralizing antibody responses of MuHV-4 carriers are improved by boosting with recombinant gH-gL. We analysed here how gH-gL-directed neutralization works. The MuHV-4 gH-gL binds to heparan sulfate. However, most gH-gL-specific neutralizing antibodies did not block this interaction; neither did they act directly on fusion. Instead, they blocked virion endocytosis and transport to the late endosomes, where membrane fusion normally occurs. The poor endocytosis of gH-gL-neutralized virions was recapitulated precisely by virions genetically lacking gL. Therefore, driving virion uptake appears to be an important function of gH-gL that provides a major target for antibody-mediated neutralization.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

