Role of Mediator in regulating Pol II elongation and nucleosome displacement in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
- PMID: 22377631
- PMCID: PMC3338273
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.111.135806
Role of Mediator in regulating Pol II elongation and nucleosome displacement in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Abstract
Mediator is a modular multisubunit complex that functions as a critical coregulator of RNA polymerase II (Pol II) transcription. While it is well accepted that Mediator plays important roles in the assembly and function of the preinitiation complex (PIC), less is known of its potential roles in regulating downstream steps of the transcription cycle. Here we use a combination of genetic and molecular approaches to investigate Mediator regulation of Pol II elongation in the model eukaryote, Saccharomyces cerevisiae. We find that ewe (expression without heat shock element) mutations in conserved Mediator subunits Med7, Med14, Med19, and Med21-all located within or adjacent to the middle module-severely diminish heat-shock-induced expression of the Hsf1-regulated HSP82 gene. Interestingly, these mutations do not impede Pol II recruitment to the gene's promoter but instead impair its transit through the coding region. This implies that a normal function of Mediator is to regulate a postinitiation step at HSP82. In addition, displacement of histones from promoter and coding regions, a hallmark of activated heat-shock genes, is significantly impaired in the med14 and med21 mutants. Suggestive of a more general role, ewe mutations confer hypersensitivity to the anti-elongation drug 6-azauracil (6-AU) and one of them-med21-impairs Pol II processivity on a GAL1-regulated reporter gene. Taken together, our results suggest that yeast Mediator, acting principally through its middle module, can regulate Pol II elongation at both heat-shock and non-heat-shock genes.
Figures


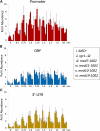


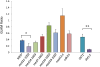
References
-
- Adkins M. W., Howar S. R., Tyler J. K., 2004. Chromatin disassembly mediated by the histone chaperone Asf1 is essential for transcriptional activation of the yeast PHO5 and PHO8 genes. Mol. Cell 14: 657–666. - PubMed
-
- Apone L. M., Virbasius C. A., Holstege F. C. P., Wang J., Young R. A., et al. , 1998. Broad, but not universal, transcriptional requirement for yTAFII17, a histone H3-like TAFII present in TFIID and SAGA. Mol. Cell 2: 653–661. - PubMed
-
- Ardehali M. B., Lis J. T., 2009. Tracking rates of transcription and splicing in vivo. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 16: 1123–1124. - PubMed
-
- Baidoobonso S. M., Guidi B. W., Myers L. C., 2007. Med19(Rox3) regulates intermodule interactions in the Saccharomyces cerevisiae Mediator complex. J. Biol. Chem. 282: 5551–5559. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

