Rapid identification of non-human sequences in high-throughput sequencing datasets
- PMID: 22377895
- PMCID: PMC3324519
- DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bts100
Rapid identification of non-human sequences in high-throughput sequencing datasets
Abstract
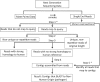
Rapid identification of non-human sequences (RINS) is an intersection-based pathogen detection workflow that utilizes a user-provided custom reference genome set for identification of non-human sequences in deep sequencing datasets. In <2 h, RINS correctly identified the known virus in the dataset SRR73726 and is compatible with any computer capable of running the prerequisite alignment and assembly programs. RINS accurately identifies sequencing reads from intact or mutated non-human genomes in a dataset and robustly generates contigs with these non-human sequences (Supplementary Material).
Availability: RINS is available for free download at http://khavarilab.stanford.edu/resources.html.
Figures