The conserved oligomeric Golgi complex is required for fucosylation of N-glycans in Caenorhabditis elegans
- PMID: 22377913
- PMCID: PMC3336869
- DOI: 10.1093/glycob/cws053
The conserved oligomeric Golgi complex is required for fucosylation of N-glycans in Caenorhabditis elegans
Abstract
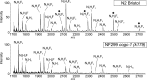
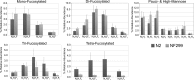
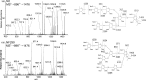
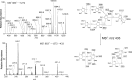
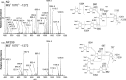
The conserved oligomeric Golgi complex (COG) is a hetero-octomeric peripheral membrane protein required for retrograde vesicular transport and glycoconjugate biosynthesis within the Golgi. Mutations in subunits 1, 4, 5, 6, 7 and 8 are the basis for a rare inheritable human disease termed congenital disorders of glycosylation type-II. Defects to COG complex function result in aberrant glycosylation, protein trafficking and Golgi structure. The cellular function of the COG complex and its role in protein glycosylation are not completely understood. In this study, we report the first detailed structural analysis of N-glycans from a COG complex-deficient organism. We employed sequential ion trap mass spectrometry of permethylated N-glycans to demonstrate that the COG complex is essential for the formation of fucose-rich N-glycans, specifically antennae fucosylated structures in Caenorhabditis elegans. Our results support the supposition that disruption to the COG complex interferes with normal protein glycosylation in the medial and/or trans-Golgi.
Figures


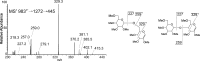


Similar articles
-
Conserved oligomeric Golgi complex specifically regulates the maintenance of Golgi glycosylation machinery.Glycobiology. 2011 Dec;21(12):1554-69. doi: 10.1093/glycob/cwr028. Epub 2011 Mar 18. Glycobiology. 2011. PMID: 21421995 Free PMC article.
-
IntraGolgi distribution of the Conserved Oligomeric Golgi (COG) complex.Exp Cell Res. 2006 Oct 1;312(16):3132-41. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2006.06.005. Epub 2006 Jun 15. Exp Cell Res. 2006. PMID: 16857184
-
COG complex-mediated recycling of Golgi glycosyltransferases is essential for normal protein glycosylation.Traffic. 2006 Feb;7(2):191-204. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2005.00376.x. Traffic. 2006. PMID: 16420527
-
Golgi inCOGnito: From vesicle tethering to human disease.Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2020 Nov;1864(11):129694. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2020.129694. Epub 2020 Jul 27. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2020. PMID: 32730773 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Conserved Oligomeric Golgi and Neuronal Vesicular Trafficking.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2018;245:227-247. doi: 10.1007/164_2017_65. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29063274 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Modeling Congenital Disorders of N-Linked Glycoprotein Glycosylation in Drosophila melanogaster.Front Genet. 2018 Oct 2;9:436. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2018.00436. eCollection 2018. Front Genet. 2018. PMID: 30333856 Free PMC article. Review.
-
N-glycomic Complexity in Anatomical Simplicity: Caenorhabditis elegans as a Non-model Nematode?Front Mol Biosci. 2019 Mar 12;6:9. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2019.00009. eCollection 2019. Front Mol Biosci. 2019. PMID: 30915340 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural and biochemical characterization of the Cutibacterium acnes exo-β-1,4-mannosidase that targets the N-glycan core of host glycoproteins.PLoS One. 2018 Sep 27;13(9):e0204703. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0204703. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30261037 Free PMC article.
-
The Golgi puppet master: COG complex at center stage of membrane trafficking interactions.Histochem Cell Biol. 2013 Sep;140(3):271-83. doi: 10.1007/s00418-013-1117-6. Epub 2013 Jul 10. Histochem Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23839779 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Towards understanding the extensive diversity of protein N-glycan structures in eukaryotes.Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2022 Apr;97(2):732-748. doi: 10.1111/brv.12820. Epub 2021 Dec 6. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2022. PMID: 34873817 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Barrows BD, Haslam SM, Bischof LJ, Morris HR, Dell A, Aroian RV. Resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis toxin in Caenorhabditis elegans from loss of fucose. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:3302–3311. doi:10.1074/jbc.M606621200. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Butschi A, Titz A, Walti MA, Olieric V, Paschinger K, Nobauer K, Guo X, Seeberger PH, Wilson IB, Aebi M, et al. Caenorhabditis elegans N-glycan core β-galactoside confers sensitivity towards nematotoxic fungal galectin CGL2. PLoS Pathog. 2010;6:e1000717. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1000717. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cavanaugh LF, Chen X, Richardson BC, Ungar D, Pelczer I, Rizo J, Hughson FM. Structural analysis of conserved oligomeric Golgi complex subunit 2. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:23418–23426. doi:10.1074/jbc.M703716200. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cipollo JF, Awad AM, Costello CE, Hirschberg CB. srf-3, a mutant of Caenorhabditis elegans, resistant to bacterial infection and to biofilm binding, is deficient in glycoconjugates. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:52893–52903. doi:10.1074/jbc.M409557200. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Conde R, Pablo G, Cueva R, Larriba G. Screening for new yeast mutants affected in mannosylphosphorylation of cell wall mannoproteins. Yeast. 2003;20:1189–1211. doi:10.1002/yea.1032. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

