Intrapulmonary administration of leukotriene B(4) augments neutrophil accumulation and responses in the lung to Klebsiella infection in CXCL1 knockout mice
- PMID: 22379035
- PMCID: PMC3311767
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1101985
Intrapulmonary administration of leukotriene B(4) augments neutrophil accumulation and responses in the lung to Klebsiella infection in CXCL1 knockout mice
Abstract
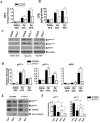
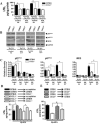
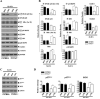
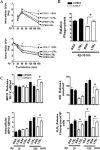
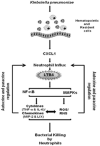
In prior studies, we demonstrated that 1) CXCL1/KC is essential for NF-κB and MAPK activation and expression of CXCL2/MIP-2 and CXCL5/LPS-induced CXC chemokine in Klebsiella-infected lungs, and 2) CXCL1 derived from hematopoietic and resident cells contributes to host immunity against Klebsiella. However, the role of CXCL1 in mediating neutrophil leukotriene B(4) (LTB(4)), reactive oxygen species (ROS), and reactive nitrogen species (RNS) production is unclear, as is the contribution of these factors to host immunity. In this study, we investigated 1) the role of CXCL1 in LTB(4), NADPH oxidase, and inducible NO synthase (iNOS) expression in lungs and neutrophils, and 2) whether LTB(4) postinfection reverses innate immune defects in CXCL1(-/-) mice via regulation of NADPH oxidase and iNOS. Our results demonstrate reduced neutrophil influx, attenuated LTB(4) levels, and decreased ROS and iNOS production in the lungs of CXCL1(-/-) mice after Klebsiella pneumoniae infection. Using neutrophil depletion and repletion, we found that neutrophils are the predominant source of pulmonary LTB(4) after infection. To treat immune defects in CXCL1(-/-) mice, we intrapulmonarily administered LTB(4). Postinfection, LTB(4) treatment reversed immune defects in CXCL1(-/-) mice and improved survival, neutrophil recruitment, cytokine/chemokine expression, NF-κB/MAPK activation, and ROS/RNS production. LTB(4) also enhanced myeloperoxidase, H(2)O(2,) RNS production, and bacterial killing in K. pneumoniae-infected CXCL1(-/-) neutrophils. These novel results uncover important roles for CXCL1 in generating ROS and RNS in neutrophils and in regulating host immunity against K. pneumoniae infection. Our findings suggest that LTB(4) could be used to correct defects in neutrophil recruitment and function in individuals lacking or expressing malfunctional CXCL1.
Figures


References
-
- Fein AM. Pneumonia in the elderly: overview of diagnostic and therapeutic approaches. Clin Infect Dis. 1999;28:726–729. - PubMed
-
- Lynch JP, 3rd, Martinez FJ. Community-acquired pneumonia. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 1998;4:162–172. - PubMed
-
- Abraham E. Neutrophils and acute lung injury. Critical Care Medicine. 2003;31:S195–S199. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

