In vitro epsilon RNA-dependent protein priming activity of human hepatitis B virus polymerase
- PMID: 22379076
- PMCID: PMC3347376
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.07137-11
In vitro epsilon RNA-dependent protein priming activity of human hepatitis B virus polymerase
Erratum in
- J Virol. 2013 Nov;87(22):12504
Abstract
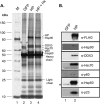
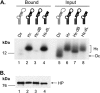
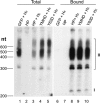
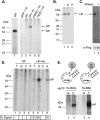
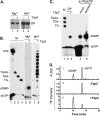
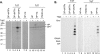
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) replicates its DNA genome through reverse transcription of a pregenomic RNA (pgRNA) by using a multifunctional polymerase (HP). A critical function of HP is its specific recognition of a viral RNA signal termed ε (Hε) located on pgRNA, which is required for specific packaging of pgRNA into viral nucleocapsids and initiation of viral reverse transcription. HP initiates reverse transcription by using itself as a protein primer (protein priming) and Hε as the obligatory template. We have purified HP from human cells that retained Hε binding activity in vitro. Furthermore, HP purified as a complex with Hε, but not HP alone, displayed in vitro protein priming activity. While the HP-Hε interaction in vitro and in vivo required the Hε internal bulge, but not its apical loop, and was not significantly affected by the cap-Hε distance, protein priming required both the Hε apical loop and internal bulge, as well as a short distance between the cap and Hε, mirroring the requirements for RNA packaging. These studies have thus established new HBV protein priming and RNA binding assays that should greatly facilitate the dissection of the requirements and molecular mechanisms of HP-Hε interactions, RNA packaging, and protein priming.
Figures
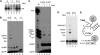

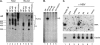

Similar articles
-
In Vitro Assays for RNA Binding and Protein Priming of Hepatitis B Virus Polymerase.Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1540:157-177. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-6700-1_13. Methods Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 27975315 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative analysis of hepatitis B virus polymerase sequences required for viral RNA binding, RNA packaging, and protein priming.J Virol. 2014 Feb;88(3):1564-72. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02852-13. Epub 2013 Nov 13. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 24227865 Free PMC article.
-
Protein-primed terminal transferase activity of hepatitis B virus polymerase.J Virol. 2013 Mar;87(5):2563-76. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02786-12. Epub 2012 Dec 19. J Virol. 2013. PMID: 23255788 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatitis B virus reverse transcriptase and its many roles in hepadnaviral genomic replication.Infect Agents Dis. 1994 Apr-Jun;3(2-3):85-93. Infect Agents Dis. 1994. PMID: 7529120 Review.
-
Hepatitis B virus reverse transcriptase - Target of current antiviral therapy and future drug development.Antiviral Res. 2015 Nov;123:132-7. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2015.09.011. Epub 2015 Sep 25. Antiviral Res. 2015. PMID: 26408354 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Unveiling the roles of HBV polymerase for new antiviral strategies.Future Virol. 2015;10(3):283-295. doi: 10.2217/fvl.14.113. Future Virol. 2015. PMID: 25893003 Free PMC article.
-
Drugging topoisomerases: lessons and challenges.ACS Chem Biol. 2013 Jan 18;8(1):82-95. doi: 10.1021/cb300648v. Epub 2013 Jan 4. ACS Chem Biol. 2013. PMID: 23259582 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sequences in the terminal protein and reverse transcriptase domains of the hepatitis B virus polymerase contribute to RNA binding and encapsidation.J Viral Hepat. 2014 Dec;21(12):882-93. doi: 10.1111/jvh.12225. Epub 2014 Jan 9. J Viral Hepat. 2014. PMID: 24401091 Free PMC article.
-
In Vitro Assays for RNA Binding and Protein Priming of Hepatitis B Virus Polymerase.Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1540:157-177. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-6700-1_13. Methods Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 27975315 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatitis B Virus Nucleocapsid Assembly.J Mol Biol. 2025 Apr 30:169182. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2025.169182. Online ahead of print. J Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 40316009 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

