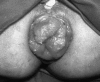
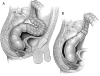
Rectal prolapse
- PMID: 22379404
- PMCID: PMC3140332
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0031-1272822
Rectal prolapse
Abstract
Rectal prolapse is a condition that usually requires surgical intervention to correct. Abdominal and perineal approaches are well described in the literature. Abdominal approaches have traditionally been reserved for young healthy patients, but this has been challenged by perineal approaches with excellent outcomes. Laparoscopic techniques have been shown to be effective and equivalent to traditional laparotomy techniques.
Keywords: Altemeier procedure; Delorme procedure; Rectal prolapse; perineal proctectomy; procidentia.
Figures
References
-
- Carley M E, Schaffer J. Urinary incontinence and pelvic organ prolapse in women with Marfan or Ehlers Danlos syndrome. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2000;182(5):1021–1023. - PubMed
-
- Karasick S, Spettell C M. The role of parity and hysterectomy on the development of pelvic floor abnormalities revealed by defecography. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1997;169(6):1555–1558. - PubMed
-
- Swift S, Woodman P, O'Boyle A, et al. Pelvic Organ Support Study (POSST): the distribution, clinical definition, and epidemiologic condition of pelvic organ support defects. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2005;192(3):795–806. - PubMed
-
- Madden M V, Kamm M A, Nicholls R J, Santhanam A N, Cabot R, Speakman C T. Abdominal rectopexy for complete prolapse: prospective study evaluating changes in symptoms and anorectal function. Dis Colon Rectum. 1992;35(1):48–55. - PubMed
-
- Madiba T E, Baig M K, Wexner S D. Surgical management of rectal prolapse. Arch Surg. 2005;140(1):63–73. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources