Irinotecan-induced dysarthria
- PMID: 22379477
- PMCID: PMC3290033
- DOI: 10.1159/000336156
Irinotecan-induced dysarthria
Abstract
Colorectal carcinomas are among the most common tumor types and are generally treated with palliative chemotherapy in case of metastatic disease. Here, we describe the case of a 46-year-old patient with metastatic rectal carcinoma who received second-line therapy with irinotecan and developed isolated transient dysarthria (with normal MR imaging of the brain) following each administration of irinotecan. Neurological and logopedical evaluation revealed that the dysarthria predominantly resulted from a reduced capacity in fine-tuning of motor functions of the tip of the tongue and a minimal reduction in the power of speech at labiodental contact. As hypoglossal nerve activity has been reported to be especially susceptible to cholinergic stimulation and irinotecan can cause cholinergic side effects by binding to and inactivating acetylcholinesterase, we suspect this mechanism to be responsible for irinotecan-induced dysarthria.
Keywords: Colorectal cancer; Dysarthria; Irinotecan.
Figures
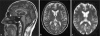
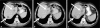
References
-
- Van Cutsem E, Twelves C, Cassidy J, et al. Oral capecitabine compared with intravenous fluorouracil plus leucovorin in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer: results of a large phase III study. J Clin Oncol. 2001;19:4097–4106. - PubMed
-
- Hoff PM, Ansari R, Batist G, et al. Comparison of oral capecitabine versus intravenous fluorouracil plus leucovorin as first-line treatment in 605 patients with metastatic colorectal cancer: results of a randomized phase III study. J Clin Oncol. 2001;19:2282–2292. - PubMed
-
- Punt CJ. Chemotherapy of patients with colorectal carcinoma. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 2005;149:1441–1447. - PubMed
-
- Hurwitz H, Fehrenbacher L, Novotny W, et al. Bevacizumab plus irinotecan, fluorouracil, and leucovorin for metastatic colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:2335–2342. - PubMed
-
- Walko CM, Lindley C. Capecitabine: a review. Clin Ther. 2005;27:23–44. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

