Macintosh laryngoscope vs. Pentax-AWS video laryngoscope: comparison of efficacy and cardiovascular responses to tracheal intubation in major burn patients
- PMID: 22379565
- PMCID: PMC3284732
- DOI: 10.4097/kjae.2012.62.2.119
Macintosh laryngoscope vs. Pentax-AWS video laryngoscope: comparison of efficacy and cardiovascular responses to tracheal intubation in major burn patients
Abstract
Background: Patients with major burns accompanied with airway edema need more attention for airway management. Although the Pentax-AWS has an advantage in managing endotracheal intubation more easily, its usefulness cannot be assured if it does not maintain hemodynamic stability in burn patients. The aim of this study was to compare cardiovascular responses and general efficacy of the Pentax-AWS and Macintosh laryngoscopes in burn patients.
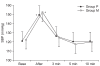
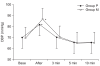
Methods: American Society of Anesthesiologists physical status 2 or 3 adult patients with major burn injury were randomly assigned to group P (AWS, n = 50) or group M (Macintosh, n = 50). Fifty-nine patients assigned to the Macintosh group and no patient to AWS group were excluded because of failure to first intubation. Hemodynamic data at baseline, just before and after intubation as well as 3, 5 and 10 minutes after intubation and grade of sore throat were recorded in two groups. Intubation time, success rate of intubation, number of intubation attempts and the percentage of glottic opening (POGO) scores were also observed and analyzed in all patients.
Results: A statistically significant increase in heart rate just after laryngoscopy was seen in group M. The success rate of the first attempt in group P (100%) was greater than with the group M (46%). POGO scores were higher in group P (97 ± 4%) than in group M (48 ± 29%)
Conclusions: The use of Pentax-AWS offers a reduced degree of heart rate elevation compared with the Macintosh laryngoscope and better intubation environments in major burn patients.
Keywords: Burns; Hemodynamics; Intratracheal; Intubation; Laryngoscopes.
Figures

References
-
- Practice guidelines for management of the difficult airway: an updated report by the American Society of Anesthesiologists task force on management of the difficult airway. Anesthesiology. 2003;98:1269–1277. - PubMed
-
- Woodson LC, Sherwood ER, Aarsland A, Talon M, Kinsky MP, Morvant EM. Anesthesia for burned patients. In: Herndon DN, editor. Total Burn Care. 3rd ed. Philadelphia: Saunders; 2007. pp. 196–228.
-
- Suzuki A, Toyama Y, Katsumi N, Kunisawa T, Sasaki R, Hirota K, et al. The Pentax-AWS rigid indirect video laryngoscope: clinical assessment of performance in 320 cases. Anaesthesia. 2008;63:641–647. - PubMed
-
- Enomoto Y, Asai T, Arai T, Kamishima K, Okuda Y. Pentax-AWS, a new videolaryngoscope, is more effective than the Macintosh laryngoscope for tracheal intubation in patients with restricted neck movements: a randomized comparative study. Br J Anaesth. 2008;100:544–548. - PubMed
-
- Asai T, Enomoto Y, Shimizu K, Shingu K, Okuda Y. The Pentax-AWS video-laryngoscope: the first experience in one hundred patients. Anesth Analg. 2008;106:257–259. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

