Default mode network abnormalities in idiopathic generalized epilepsy
- PMID: 22381387
- PMCID: PMC4407647
- DOI: 10.1016/j.yebeh.2012.01.013
Default mode network abnormalities in idiopathic generalized epilepsy
Abstract
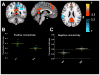
Idiopathic generalized epilepsy (IGE) is associated with widespread cortical network abnormalities on electroencephalography. Resting state functional connectivity (RSFC), based on fMRI, can assess the brain's global functional organization and its disruption in clinical conditions. We compared RSFC associated with the 'default mode network' (DMN) between people with IGE and healthy controls. Strength of functional connectivity within the DMN associated with seeds in the posterior cingulate cortex (PCC) and medial prefrontal cortices (MPFC) was compared between people with IGE and healthy controls and was correlated with seizure duration, age of seizure onset and age at scan. Those with IGE showed markedly reduced functional network connectivity between anterior and posterior cortical seed regions. Seizure duration positively correlates with RSFC between parahippocampal gyri and the PCC but negatively correlates with connectivity between the PCC and frontal lobe. The observed pattern of disruption provides evidence for integration- and segregation-type network abnormalities and supports aberrant network organization among people with IGE.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest disclosure:
None of the authors has any conflicts of interest to disclose. We confirm that we have read the Journal’s position on issues involved in ethical publication and affirm that this report is consistent with those guidelines.
Similar articles
-
Dynamic functional network connectivity in idiopathic generalized epilepsy with generalized tonic-clonic seizure.Hum Brain Mapp. 2017 Feb;38(2):957-973. doi: 10.1002/hbm.23430. Epub 2016 Oct 11. Hum Brain Mapp. 2017. PMID: 27726245 Free PMC article.
-
Increased cortical BOLD signal anticipates generalized spike and wave discharges in adolescents and adults with idiopathic generalized epilepsies.Epilepsia. 2012 Apr;53(4):622-30. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1167.2011.03385.x. Epub 2012 Jan 13. Epilepsia. 2012. PMID: 22242887
-
Impairments of cingulated cortex in the generalized tonic-clonic seizure epilepsy by combining morphological and functional connectivity magnetic resonance imaging.J Integr Neurosci. 2017;16(4):429-439. doi: 10.3233/JIN-170026. J Integr Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28891522
-
Integration and Segregation of Default Mode Network Resting-State Functional Connectivity in Transition-Age Males with High-Functioning Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Proof-of-Concept Study.Brain Connect. 2017 Nov;7(9):558-573. doi: 10.1089/brain.2016.0483. Brain Connect. 2017. PMID: 28942672 Free PMC article.
-
Altered functional connectivity among default, attention, and control networks in idiopathic generalized epilepsy.Epilepsy Behav. 2015 May;46:118-25. doi: 10.1016/j.yebeh.2015.03.031. Epub 2015 Apr 30. Epilepsy Behav. 2015. PMID: 25935514
Cited by
-
Comparison of Resting-State EEG Network Analyses With and Without Parallel MRI in Genetic Generalized Epilepsy.Brain Topogr. 2023 Sep;36(5):750-765. doi: 10.1007/s10548-023-00977-6. Epub 2023 Jun 24. Brain Topogr. 2023. PMID: 37354244 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamical Network Models From EEG and MEG for Epilepsy Surgery-A Quantitative Approach.Front Neurol. 2022 Mar 29;13:837893. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.837893. eCollection 2022. Front Neurol. 2022. PMID: 35422755 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identifying the neural network for neuromodulation in epilepsy through connectomics and graphs.Brain Commun. 2022 Apr 6;4(3):fcac092. doi: 10.1093/braincomms/fcac092. eCollection 2022. Brain Commun. 2022. PMID: 35611305 Free PMC article.
-
Neuronal network models of epileptogenesis.Neurosciences (Riyadh). 2017 Apr;22(2):85-93. doi: 10.17712/nsj.2017.2.20160455. Neurosciences (Riyadh). 2017. PMID: 28416779 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Altered effective connectivity of the default mode network in juvenile myoclonic epilepsy.Cogn Neurodyn. 2024 Aug;18(4):1549-1561. doi: 10.1007/s11571-023-09994-4. Epub 2023 Jul 31. Cogn Neurodyn. 2024. PMID: 39104702 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gloor P. Generalized epilepsy with bilateral synchronous spike and wave discharge. New findings concerning its physiological mechanisms. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol Suppl. 1978:245–9. - PubMed
-
- Tyvaert L, Chassagnon S, Sadikot A, LeVan P, Dubeau F, Gotman J. Thalamic nuclei activity in idiopathic generalized epilepsy: an EEG_fMRI study. Neurology. 2009;73:2018–22. - PubMed
-
- Buzsaki G, Draguhn A. Neuronal oscillations in cortical networks. Science. 2004;304:7709–17. - PubMed
-
- Biswal B, Yetkin FZ, Haughton VM, Hyde JS. Functional connectivity in the motor cortex of resting human brain using echo-planar MRI. Magn Reson Med. 1995;34:537–41. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources