Biosynthesis of pyrrolopyrimidines
- PMID: 22382038
- PMCID: PMC4022189
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2012.01.001
Biosynthesis of pyrrolopyrimidines
Abstract
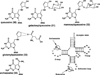
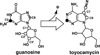
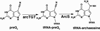
Pyrrolopyrimidine containing compounds, also known as 7-deazapurines, are a collection of purine-based metabolites that have been isolated from a variety of biological sources and have diverse functions which range from secondary metabolism to RNA modification. To date, nearly 35 compounds with the common 7-deazapurine core structure have been described. This article will illustrate the structural diversity of these compounds and review the current state of knowledge on the biosynthetic pathways that give rise to them.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

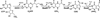
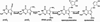
References
-
- Nishimura H, Katagiri K, Sato K, Mayama M, Shimaoka N. Toyocamycin, a new anti-candida antibiotics. J. Antibiot. 1956;9:60–62. - PubMed
-
- Waksman S. Streptomycin: background, isolation, properties, and utilization. Science. 1953;118:259–266. - PubMed
-
- Tolman RL, Robins RK, Townsend LB. Pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine nucleoside antibiotics. Total synthesis and structure of toyocamycin, unamycin B, vengicide, antibiotic E-212, and Sangivamycin (BA-90912) J Am Chem Soc. 1968;90:524–526. - PubMed
-
- Anzai K, Nakamura G, Suzuki S. A new antibiotic, tubercidin. J. Antibiot. 1957;10:201–204. - PubMed
-
- Rao K, Renn D. BA-90912: An antitumor substance. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (Bethesda) 1963;161:77–79. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

