Increased percentage of T cells with the expression of CD127 and CD132 in hypertrophic adenoid in children with otitis media with effusion
- PMID: 22382400
- PMCID: PMC3365238
- DOI: 10.1007/s00405-012-1977-8
Increased percentage of T cells with the expression of CD127 and CD132 in hypertrophic adenoid in children with otitis media with effusion
Abstract
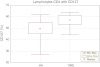
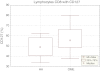
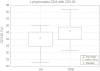
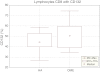
The hypertrophic adenoid may promote chronic suppurative otitis media in children as it fulfills its immune function. The number of lymphocytes in the adenoid and their cooperation in the immune response depend of on their proliferation and migration to the effector sites. Interleukin 7 (IL-7) is essential for the normal development and function lymphocytes. IL-7 plays pivotal role for activation and proliferation of T and B cells. The heterodimeric interleukin-7 receptor (IL-7R) is composed of the IL-7Rα (127) and the common cytokine receptor γc (CD132). The aim of this study was to evaluate the percentage of lymphocytes T (CD4(+) and CD8(+)) with IL-7R (CD127 and CD132) expression in hypertrophic adenoid in children suffering with otitis media with effusion for a duration of 3 months. Adenoid excised due to hypertrophy with or without chronic otitis media with effusion was used as study material. CD4(+) CD127(+), CD4(+)132(+), CD8(+)CD127(+) and CD8(+)CD132(+) cell subpopulations were identified using monoclonal antibodies and flow cytometry. The percentage of CD4(+) and CD8(+) T cells with CD127 receptor expression in hypertrophic adenoid of children with otitis media with effusion was statistically significantly higher than in hypertrophic adenoid group. The percentage of CD4(+) T cells with CD132 expression in the study group was statistically significantly higher than in the reference group. The percentage of CD8(+) T cells with CD132(+) expression was not statistically different in both groups. The increased percentage of T lymphocytes with IL-7R expression (CD127 and CD132) in hypertrophic adenoid seems to influence the quantity of lymphocytes and upset the immunological function of tonsils which can influence the course of otitis media with effusion.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[The cytofluorometric opinion of expression of adhesion molecules CD11a and CD54 on lymphocytes T and B in children's hypertrophied adenoids, which are sick on the otitis media with effusion].Otolaryngol Pol. 2006;60(4):565-70. Otolaryngol Pol. 2006. PMID: 17152810 Polish.
-
[Expression Fas and FasL antigen protein of lymphocytes T and B in hypertrophied adenoid in children with otitis media with effusion].Otolaryngol Pol. 2008;62(1):59-64. doi: 10.1016/S0030-6657(08)70210-5. Otolaryngol Pol. 2008. PMID: 18637423 Polish.
-
Chosen factors of T and B cell apoptosis in hypertrophic adenoid in children with otitis media with effusion.Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2010 Jun;74(6):698-700. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2010.02.024. Epub 2010 Mar 24. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2010. PMID: 20338643
-
Otitis media and tonsils--role of adenoidectomy in the treatment of chronic otitis media with effusion.Adv Otorhinolaryngol. 2011;72:160-3. doi: 10.1159/000324781. Epub 2011 Aug 18. Adv Otorhinolaryngol. 2011. PMID: 21865719 Review.
-
The influence of HIV on CD127 expression and its potential implications for IL-7 therapy.Semin Immunol. 2012 Jun;24(3):231-40. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2012.02.006. Epub 2012 Mar 14. Semin Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22421574 Review.
Cited by
-
IL-15 promotes self-renewal of progenitor exhausted CD8 T cells during persistent antigenic stimulation.Front Immunol. 2023 Jun 20;14:1117092. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1117092. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37409128 Free PMC article.
-
Otitis media with effusion in preschool children with adenoid hypertrophy: Risk factors and nursing care.Nurs Open. 2024 May;11(5):e2165. doi: 10.1002/nop2.2165. Nurs Open. 2024. PMID: 38701327 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of T follicular helper cells in the pathogenesis of adenoidal hypertrophy combined with secretory otitis media.Medicine (Baltimore). 2018 Mar;97(13):e0211. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000010211. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018. PMID: 29595664 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of the T-cell subpopulations in the granulation tissues of chronic suppurative otitis media.Biomed Rep. 2016 Jun;4(6):694-698. doi: 10.3892/br.2016.657. Epub 2016 Apr 18. Biomed Rep. 2016. PMID: 27313854 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fry TJ, Mackall CL. The many faces of IL-7, from lymphopoiesis to peripheral T cell maintenance. J Immunol. 2005;174(11):6571–6576. - PubMed
-
- Giliani S, Mori L, de Saint Basile G, Le Deist F, Rodriguez-Perez C, Forrino C, Mazzolani E, Dupuis S, Elhasid R, Kessel A, Galambrun C, Gil J, Fischer A, Etzioni A, Notarangelo LD. Interleukin-7 receptor α (IL-Rα) deficiency: cellular and molecular bases. Analysis of clinical, immunological, and molecular features in 16 novel patients. Immunol Rev. 2005;203:110–126. doi: 10.1111/j.0105-2896.2005.00234.x. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

