Pleiotrophin expression during odontogenesis
- PMID: 22382872
- PMCID: PMC3351233
- DOI: 10.1369/0022155412439316
Pleiotrophin expression during odontogenesis
Abstract
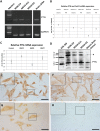
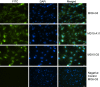
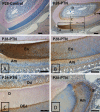
Pleiotrophin (PTN) is an extracellular matrix-associated growth factor and chemokine expressed in mesodermal and ectodermal cells. It plays an important role in osteoblast recruitment and differentiation. There is limited information currently available about PTN expression during odontoblast differentiation and tooth formation, and thus the authors aimed to establish the spatiotemporal expression pattern of PTN during mouse odontogenesis. Immortalized mouse dental pulp (MD10-D3, MD10-A11) and odontoblast-like (M06-G3) and ameloblast-like (EOE-3M) cell lines were grown and samples prepared for immunocytochemistry, Western blot, and conventional and quantitative PCR analysis. Effects of BMP2, BMP4, and BMP7 treatment on PTN expression in odontoblast-like M06-G3 cells were tested by quantitative PCR. Finally, immunohistochemistry of sectioned mice mandibles and maxillaries at developmental stages E16, E18, P1, P6, P10, and P28 was performed. The experiments showed that PTN, at both the mRNA and protein level, was expressed in all tested epithelial and mesenchymal dental cell lines and that the level of PTN mRNA was influenced differentially by the bone morphogenetic proteins. The authors observed initial expression of PTN in the inner enamel epithelium with prolonged expression in the ameloblasts and odontoblasts throughout their stages of maturation and strong expression in the terminally differentiated and enamel matrix-secreting ameloblasts and odontoblasts of the adult mouse incisors and molars.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures


References
-
- Arai H, Higuchi S, Muramatsu T, Iwatsubo T, Sasaki H, Trojanowski JQ. 1994. Apolipoprotein E gene in diffuse Lewy body disease with or without co-existing Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet. 344(8932):1307 - PubMed
-
- Bernard-Pierrot I, Heroult M, Lemaitre G, Barritault D, Courty J, Milhiet PE. 1999. Glycosaminoglycans promote HARP/PTN dimerization. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 266(2):437–442 - PubMed
-
- Deuel TF, Zhang N, Yeh HJ, Silos-Santiago I, Wang ZY. 2002. Pleiotrophin: a cytokine with diverse functions and a novel signaling pathway. Arch Biochem Biophys. 397(2):162–171 - PubMed
-
- Hamma-Kourbali Y, Bernard-Pierrot I, Heroult M, Dalle S, Caruelle D, Milhiet PE, Fernig DG, Delbe J, Courty J. 2008. Inhibition of the mitogenic, angiogenic and tumorigenic activities of pleiotrophin by a synthetic peptide corresponding to its C-thrombospondin repeat-I domain. J Cell Physiol. 214(1):250–259 - PubMed
-
- Hikake T, Mori T, Iseki K, Hagino S, Zhang Y, Takagi H, Yokoya S, Wanaka A. 2003. Comparison of expression patterns between CREB family transcription factor OASIS and proteoglycan core protein genes during murine tooth development. Anat Embryol (Berl). 206(5):373–380 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

