Reduced-distortion diffusion MRI of the craniovertebral junction
- PMID: 22383239
- PMCID: PMC7965517
- DOI: 10.3174/ajnr.A2969
Reduced-distortion diffusion MRI of the craniovertebral junction
Abstract
Background and purpose: CVJ lesion suffers from a high sensitivity to susceptibility and distortion artifacts, which sometimes makes diffusion image difficult to interpret. Our purpose was to evaluate the potential for diffusion MR imaging using RS-EPI compared with SS-EPI in the assessment of the CVJ.
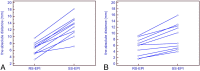
Materials and methods: RS-EPI and SS-EPI DTI images were acquired from 10 healthy volunteers using 3T MRI with a 32-channel head coil. For both sequences, the following parameters were used: 1-mm(2) in-plane resolution; 3-mm section thickness; TR = 5200 ms; 1 acquisition at b = 0 and 12 different encoding directions at b = 1000 seconds/mm(2). The RS-EPI sequence scan time was 9.44 minutes (1 average). The SS-EPI sequence was 9.37 minutes (8 averages). Diffusion tensor calculation and image analysis were performed using DTIStudio software. Diffusion trace images and color-coded fiber orientation maps were evaluated by 2 independent readers for distortion and delineation of fine structure using a semiquantitative scale in selected landmark locations. The absolute distances between the temporal base and the cerebellar contour between the T2-weighted images and the diffusion trace images obtained with RS-EPI and SS-EPI were also compared.
Results: The contours of the temporal lobe and cerebellum were better delineated and distortion artifacts were clearly reduced with the RS-EPI sequence. More fine structures were also visible in the brain stem and cerebellum with the RS-EPI sequence. The amount of distortion was significantly reduced with RS-EPI compared with SS-EPI (P < .01).
Conclusions: The RS-EPI DTI sequence was less prone to geometric distortion than the SS-EPI sequence and allowed a better delineation of CVJ internal structure. Although the acquisition time is still relatively long, the RS-EPI appears as a promising approach to perform DTI studies in CVJ lesions, such as brain stem ischemia, neurodegenerative diseases, brain and skull base tumors, or inflammation.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Readout-segmented echo-planar imaging for diffusion-weighted imaging in the pelvis at 3T-A feasibility study.Acad Radiol. 2014 Apr;21(4):531-7. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2014.01.005. Acad Radiol. 2014. PMID: 24594423
-
Diffusion-weighted imaging in patients with acute brain ischemia at 3 T: current possibilities and future perspectives comparing conventional echoplanar diffusion-weighted imaging and fast spin echo diffusion-weighted imaging sequences using BLADE (PROPELLER).Invest Radiol. 2009 Jun;44(6):351-9. doi: 10.1097/RLI.0b013e3181a00d09. Invest Radiol. 2009. PMID: 19363447
-
Diffusion-sensitized ophthalmic magnetic resonance imaging free of geometric distortion at 3.0 and 7.0 T: a feasibility study in healthy subjects and patients with intraocular masses.Invest Radiol. 2015 May;50(5):309-21. doi: 10.1097/RLI.0000000000000129. Invest Radiol. 2015. PMID: 25612144
-
Reproducibility and feasibility of optic nerve diffusion MRI techniques: single-shot echo-planar imaging (EPI), readout-segmented EPI, and reduced field-of-view diffusion-weighted imaging.BMC Med Imaging. 2022 May 24;22(1):96. doi: 10.1186/s12880-022-00814-5. BMC Med Imaging. 2022. PMID: 35606748 Free PMC article.
-
Challenges of High-resolution Diffusion Imaging of the Human Medial Temporal Lobe in Alzheimer Disease.Top Magn Reson Imaging. 2010 Dec;21(6):355-65. doi: 10.1097/RMR.0b013e31823f6413. Top Magn Reson Imaging. 2010. PMID: 22158129 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Diffusion-weighted imaging of skull lesions.J Neurol Surg B Skull Base. 2014 Jun;75(3):204-13. doi: 10.1055/s-0034-1371362. Epub 2014 Mar 12. J Neurol Surg B Skull Base. 2014. PMID: 25072014 Free PMC article.
-
White matter tractography for neurosurgical planning: A topography-based review of the current state of the art.Neuroimage Clin. 2017 Jun 15;15:659-672. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2017.06.011. eCollection 2017. Neuroimage Clin. 2017. PMID: 28664037 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The clinical utility of reduced-distortion readout-segmented echo-planar imaging in the head and neck region: initial experience.Eur Radiol. 2014 Dec;24(12):3088-96. doi: 10.1007/s00330-014-3369-5. Epub 2014 Aug 13. Eur Radiol. 2014. PMID: 25117744
-
CSF Pulsation Artifacts on ADC Maps Obtained with Readout-segmented EPI.Magn Reson Med Sci. 2017 Apr 10;16(2):123-128. doi: 10.2463/mrms.mp.2016-0031. Epub 2016 Jul 13. Magn Reson Med Sci. 2017. PMID: 27430484 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of Apparent Diffusion Coefficients of the Brain in Healthy Controls: A Comparison Study between Single-Shot Echo-Planar Imaging and Read-out-Segmented Echo-Planar Imaging.Korean J Radiol. 2019 Jul;20(7):1138-1145. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2018.0899. Korean J Radiol. 2019. PMID: 31270977 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Le Bihan D.. Looking into the functional architecture of the brain with diffusion MRI. Nat Rev Neurosci 2003;4:469–80 - PubMed
-
- Sundgren P, Dong Q, Gomez-Hassan D, et al. . Diffusion tensor imaging of the brain: review of clinical applications. Neuroradiology 2004;46:339–50 - PubMed
-
- Forbes KP, Pipe JG, Karis JP, et al. . Improved image quality and detection of acute cerebral infarction with PROPELLER diffusion-weighted MR imaging. Radiology 2002;225:551–55 - PubMed
-
- Le Bihan D, Mangin JF, Poupon C, et al. . Diffusion tensor imaging: concepts and applications. J Magn Reson Imaging 2001;13:534–46 - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
