Yeast mitochondrial leucyl-tRNA synthetase CP1 domain has functionally diverged to accommodate RNA splicing at expense of hydrolytic editing
- PMID: 22383526
- PMCID: PMC3340235
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M111.322412
Yeast mitochondrial leucyl-tRNA synthetase CP1 domain has functionally diverged to accommodate RNA splicing at expense of hydrolytic editing
Abstract
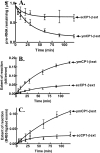
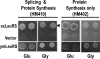
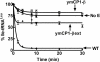
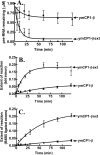
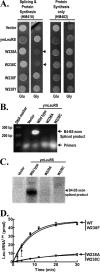
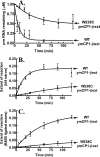
The yeast mitochondrial leucyl-tRNA synthetase (ymLeuRS) performs dual essential roles in group I intron splicing and protein synthesis. A specific LeuRS domain called CP1 is responsible for clearing noncognate amino acids that are misactivated during aminoacylation. The ymLeuRS CP1 domain also plays a critical role in splicing. Herein, the ymLeuRS CP1 domain was isolated from the full-length enzyme and was active in RNA splicing in vitro. Unlike its Escherichia coli LeuRS CP1 domain counterpart, it failed to significantly hydrolyze misaminoacylated tRNA(Leu). In addition and in stark contrast to the yeast domain, the editing-active E. coli LeuRS CP1 domain failed to recapitulate the splicing activity of the full-length E. coli enzyme. Although LeuRS-dependent splicing activity is rooted in an ancient adaptation for its aminoacylation activity, these results suggest that the ymLeuRS has functionally diverged to confer a robust splicing activity. This adaptation could have come at some expense to the protein's housekeeping role in aminoacylation and editing.
Figures

References
-
- Lambowitz A. M., Perlman P. S. (1990) Involvement of aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases and other proteins in group I and group II intron splicing. Trends Biochem. Sci. 15, 440–444 - PubMed
-
- Ibba M., Soll D. (2000) Aminoacyl-tRNA synthesis. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 69, 617–650 - PubMed
-
- Labouesse M. (1990) The yeast mitochondrial leucyl-tRNA synthetase is a splicing factor for the excision of several group I introns. Mol. Gen. Genet. 224, 209–221 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

