Characterization of EHop-016, novel small molecule inhibitor of Rac GTPase
- PMID: 22383527
- PMCID: PMC3339933
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M111.334524
Characterization of EHop-016, novel small molecule inhibitor of Rac GTPase
Abstract
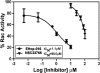
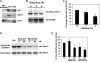
The Rho GTPase Rac regulates actin cytoskeleton reorganization to form cell surface extensions (lamellipodia) required for cell migration/invasion during cancer metastasis. Rac hyperactivation and overexpression are associated with aggressive cancers; thus, interference of the interaction of Rac with its direct upstream activators, guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs), is a viable strategy for inhibiting Rac activity. We synthesized EHop-016, a novel inhibitor of Rac activity, based on the structure of the established Rac/Rac GEF inhibitor NSC23766. Herein, we demonstrate that EHop-016 inhibits Rac activity in the MDA-MB-435 metastatic cancer cells that overexpress Rac and exhibits high endogenous Rac activity. The IC(50) of 1.1 μM for Rac inhibition by EHop-016 is ∼100-fold lower than for NSC23766. EHop-016 is specific for Rac1 and Rac3 at concentrations of ≤5 μM. At higher concentrations, EHop-016 inhibits the close homolog Cdc42. In MDA-MB-435 cells that demonstrate high active levels of the Rac GEF Vav2, EHop-016 inhibits the association of Vav2 with a nucleotide-free Rac1(G15A), which has a high affinity for activated GEFs. EHop-016 also inhibits the Rac activity of MDA-MB-231 metastatic breast cancer cells and reduces Rac-directed lamellipodia formation in both cell lines. EHop-016 decreases Rac downstream effects of PAK1 (p21-activated kinase 1) activity and directed migration of metastatic cancer cells. Moreover, at effective concentrations (<5 μM), EHop-016 does not affect the viability of transformed mammary epithelial cells (MCF-10A) and reduces viability of MDA-MB-435 cells by only 20%. Therefore, EHop-016 holds promise as a targeted therapeutic agent for the treatment of metastatic cancers with high Rac activity.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Development of EHop-016: a small molecule inhibitor of Rac.Enzymes. 2013;33 Pt A(Pt A):117-46. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-416749-0.00006-3. Epub 2013 Aug 8. Enzymes. 2013. PMID: 25033803 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterization of a Dual Rac/Cdc42 Inhibitor MBQ-167 in Metastatic Cancer.Mol Cancer Ther. 2017 May;16(5):805-818. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-16-0442. Mol Cancer Ther. 2017. PMID: 28450422 Free PMC article.
-
Novel inhibitors of Rac1 in metastatic breast cancer.P R Health Sci J. 2010 Dec;29(4):348-56. P R Health Sci J. 2010. PMID: 21261173
-
Rational design and characterization of a Rac GTPase-specific small molecule inhibitor.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 May 18;101(20):7618-23. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0307512101. Epub 2004 May 5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004. PMID: 15128949 Free PMC article.
-
Structure-function based design of small molecule inhibitors targeting Rho family GTPases.Curr Top Med Chem. 2006;6(11):1109-16. doi: 10.2174/156802606777812095. Curr Top Med Chem. 2006. PMID: 16842149 Review.
Cited by
-
Rac1, A Potential Target for Tumor Therapy.Front Oncol. 2021 May 17;11:674426. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.674426. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34079763 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rac inhibition as a novel therapeutic strategy for EGFR/HER2 targeted therapy resistant breast cancer.BMC Cancer. 2021 Jun 1;21(1):652. doi: 10.1186/s12885-021-08366-7. BMC Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34074257 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Cancer by Using Nanoparticles to Modulate RHO GTPase Signaling.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2022;1357:115-127. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-88071-2_5. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2022. PMID: 35583642
-
Therapeutic Targeting the Allosteric Cysteinome of RAS and Kinase Families.J Mol Biol. 2022 Sep 15;434(17):167626. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2022.167626. Epub 2022 May 18. J Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 35595166 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dysregulation of Rho GTPases in Human Cancers.Cancers (Basel). 2020 May 7;12(5):1179. doi: 10.3390/cancers12051179. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32392742 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

