Identification of a cis-acting element that localizes mRNA to synapses
- PMID: 22383561
- PMCID: PMC3311331
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1116269109
Identification of a cis-acting element that localizes mRNA to synapses
Abstract
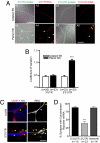
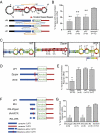
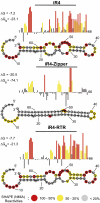
Messenger RNA (mRNA) localization and regulated translation can spatially restrict gene expression to each of the thousands of synaptic compartments formed by a single neuron. Although cis-acting RNA elements have been shown to direct localization of mRNAs from the soma into neuronal processes, less is known about signals that target transcripts specifically to synapses. In Aplysia sensory-motor neuronal cultures, synapse formation rapidly redistributes the mRNA encoding the peptide neurotransmitter sensorin from neuritic shafts into synapses. We find that the export of sensorin mRNA from soma to neurite and the localization to synapse are controlled by distinct signals. The 3' UTR is sufficient for export into distal neurites, whereas the 5' UTR is required for concentration of reporter mRNA at synapses. We have identified a 66-nt element in the 5' UTR of sensorin that is necessary and sufficient for synaptic mRNA localization. Mutational and chemical probing analyses are consistent with a role for secondary structure in this process.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Synapse formation and mRNA localization in cultured Aplysia neurons.Neuron. 2006 Feb 2;49(3):349-56. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2005.12.029. Neuron. 2006. PMID: 16446139
-
Target interaction regulates distribution and stability of specific mRNAs.J Neurosci. 2002 Apr 1;22(7):2669-78. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-07-02669.2002. J Neurosci. 2002. PMID: 11923432 Free PMC article.
-
Target-dependent release of a presynaptic neuropeptide regulates the formation and maturation of specific synapses in Aplysia.J Neurosci. 2004 Nov 3;24(44):9933-43. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3329-04.2004. J Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 15525778 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of the cis-acting element directing perinuclear localization of the metallothionein-1 mRNA.Biochem Soc Trans. 2004 Nov;32(Pt 5):702-4. doi: 10.1042/BST0320702. Biochem Soc Trans. 2004. PMID: 15493992 Review.
-
Conservation of a core neurite transcriptome across neuronal types and species.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2020 Jul;11(4):e1590. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1590. Epub 2020 Feb 14. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2020. PMID: 32059075 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of 3' UTR motifs required for mRNA localization to myelin sheaths in vivo.PLoS Biol. 2021 Jan 13;19(1):e3001053. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3001053. eCollection 2021 Jan. PLoS Biol. 2021. PMID: 33439856 Free PMC article.
-
Proteogenomics of synaptosomal mitochondrial oxidative stress.Free Radic Biol Med. 2012 Sep 1;53(5):1048-60. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2012.07.004. Epub 2012 Jul 13. Free Radic Biol Med. 2012. PMID: 22796328 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct cis elements in the 3' UTR of the C. elegans cebp-1 mRNA mediate its regulation in neuronal development.Dev Biol. 2017 Sep 1;429(1):240-248. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2017.06.022. Epub 2017 Jun 30. Dev Biol. 2017. PMID: 28673818 Free PMC article.
-
Proteostasis and RNA Binding Proteins in Synaptic Plasticity and in the Pathogenesis of Neuropsychiatric Disorders.Neural Plast. 2016;2016:3857934. doi: 10.1155/2016/3857934. Epub 2016 Jan 12. Neural Plast. 2016. PMID: 26904297 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DM3Loc: multi-label mRNA subcellular localization prediction and analysis based on multi-head self-attention mechanism.Nucleic Acids Res. 2021 May 7;49(8):e46. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkab016. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021. PMID: 33503258 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Eberwine J, Belt B, Kacharmina JE, Miyashiro K. Analysis of subcellularly localized mRNAs using in situ hybridization, mRNA amplification, and expression profiling. Neurochem Res. 2002;27:1065–1077. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

