Identification of gene mutations in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease through targeted resequencing
- PMID: 22383692
- PMCID: PMC3338301
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2011101032
Identification of gene mutations in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease through targeted resequencing
Abstract
Mutations in two large multi-exon genes, PKD1 and PKD2, cause autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD). The duplication of PKD1 exons 1-32 as six pseudogenes on chromosome 16, the high level of allelic heterogeneity, and the cost of Sanger sequencing complicate mutation analysis, which can aid diagnostics of ADPKD. We developed and validated a strategy to analyze both the PKD1 and PKD2 genes using next-generation sequencing by pooling long-range PCR amplicons and multiplexing bar-coded libraries. We used this approach to characterize a cohort of 230 patients with ADPKD. This process detected definitely and likely pathogenic variants in 115 (63%) of 183 patients with typical ADPKD. In addition, we identified atypical mutations, a gene conversion, and one missed mutation resulting from allele dropout, and we characterized the pattern of deep intronic variation for both genes. In summary, this strategy involving next-generation sequencing is a model for future genetic characterization of large ADPKD populations.
Figures





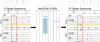

References
-
- Dalgaard OZ: Bilateral polycystic disease of the kidneys; a follow-up of two hundred and eighty-four patients and their families. Acta Med Scand Suppl 328: 1–255, 1957 - PubMed
-
- Iglesias CG, Torres VE, Offord KP, Holley KE, Beard CM, Kurland LT: Epidemiology of adult polycystic kidney disease, Olmsted County, Minnesota: 1935-1980. Am J Kidney Dis 2: 630–639, 1983 - PubMed
-
- Rossetti S, Consugar MB, Chapman AB, Torres VE, Guay-Woodford LM, Grantham JJ, Bennett WM, Meyers CM, Walker DL, Bae K, Zhang QJ, Thompson PA, Miller JP, Harris PC, CRISP Consortium : Comprehensive molecular diagnostics in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. J Am Soc Nephrol 18: 2143–2160, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Ravine D, Walker RG, Gibson RN, Forrest SM, Richards RI, Friend K, Sheffield LJ, Kincaid-Smith P, Danks DM: Phenotype and genotype heterogeneity in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Lancet 340: 1330–1333, 1992 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

