Tim-3 marks human natural killer cell maturation and suppresses cell-mediated cytotoxicity
- PMID: 22383801
- PMCID: PMC3335380
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2011-11-392951
Tim-3 marks human natural killer cell maturation and suppresses cell-mediated cytotoxicity
Abstract
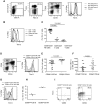
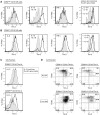
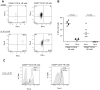
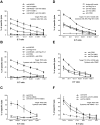
Natural killer (NK) cells are innate lymphocytes that play an important role against viral infections and cancer. This effect is achieved through a complex mosaic of inhibitory and activating receptors expressed by NK cells that ultimately determine the magnitude of the NK-cell response. The T-cell immunoglobulin- and mucin domain-containing (Tim)-3 receptor was initially identified as a T-helper 1-specific type I membrane protein involved in regulating T-cell responses. Human NK cells transcribe the highest amounts of Tim-3 among lymphocytes. Tim-3 protein is expressed on essentially all mature CD56(dim)CD16(+) NK cells and is expressed heterogeneously in the immature CD56(bright)CD16(-) NK-cell subset in blood from healthy adults and in cord blood. Tim-3 expression was induced on CD56(bright)CD16(-) NK cells after stimulation with IL-15 or IL-12 and IL-18 in vitro, suggesting that Tim-3 is a maturation marker on NK cells. Whereas Tim-3 has been used to identify dysfunctional T cells, NK cells expressing high amounts of Tim-3 are fully responsive with respect to cytokine production and cytotoxicity. However, when Tim-3 was cross-linked with antibodies it suppressed NK cell-mediated cytotoxicity. These findings suggest that NK-cell responses may be negatively regulated when NK cells encounter target cells expressing cognate ligands of Tim-3.
Figures

References
-
- Vilches C, Parham P. KIR: diverse, rapidly evolving receptors of innate and adaptive immunity. Annu Rev Immunol. 2002;20:217–251. - PubMed
-
- Cooper MA, Fehniger TA, Caligiuri MA. The biology of human natural killer-cell subsets. Trends Immunol. 2001;22(11):633–640. - PubMed
-
- Lanier LL, Le AM, Civin CI, Loken MR, Phillips JH. The relationship of CD16 (Leu-11) and Leu-19 (NKH-1) antigen expression on human peripheral blood NK cells and cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1986;136(12):4480–4486. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R21 AI060379/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI68498/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI076014/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI64520/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AI083112/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI068498/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI076014/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI080129/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K01 AI066917/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI068129/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI064520/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI066917/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI60379/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI080129/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI083112/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI060379/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI027763/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI068129/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

