Identification of the social and cognitive processes underlying human cumulative culture
- PMID: 22383851
- PMCID: PMC4676561
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1213969
Identification of the social and cognitive processes underlying human cumulative culture
Abstract
The remarkable ecological and demographic success of humanity is largely attributed to our capacity for cumulative culture, with knowledge and technology accumulating over time, yet the social and cognitive capabilities that have enabled cumulative culture remain unclear. In a comparative study of sequential problem solving, we provided groups of capuchin monkeys, chimpanzees, and children with an experimental puzzlebox that could be solved in three stages to retrieve rewards of increasing desirability. The success of the children, but not of the chimpanzees or capuchins, in reaching higher-level solutions was strongly associated with a package of sociocognitive processes-including teaching through verbal instruction, imitation, and prosociality-that were observed only in the children and covaried with performance.
Figures
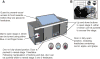
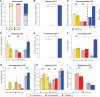
Comment in
-
Behavior. Origins of cumulative culture.Science. 2012 Mar 2;335(6072):1056-7. doi: 10.1126/science.1219232. Science. 2012. PMID: 22383839 No abstract available.
References
-
- Boyd R, Richerson P. Culture and the Evolutionary Process. Univ of Chicago Press; Chicago: 1985.
-
- Tomasello M. In: Chimpanzee Cultures. Wrangham RW, McGrew WC, de Waal FBM, Heltne PG, editors. Harvard Univ Press; Cambridge, MA: 1994. pp. 301–377.
-
- Enquist M, Ghirlanda S. J Theor Biol. 2007;246:129. - PubMed
-
- Boyd R, Richerson P. Proc Br Acad. 1996;88:77.
-
- Galef BG. Hum Nat. 1992;3:157. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

