Delayed cutaneous wound healing and aberrant expression of hair follicle stem cell markers in mice selectively lacking Ctip2 in epidermis
- PMID: 22383956
- PMCID: PMC3283611
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0029999
Delayed cutaneous wound healing and aberrant expression of hair follicle stem cell markers in mice selectively lacking Ctip2 in epidermis
Abstract
Background: COUP-TF interacting protein 2 [(Ctip2), also known as Bcl11b] is an important regulator of skin homeostasis, and is overexpressed in head and neck cancer. Ctip2(ep-/-) mice, selectively ablated for Ctip2 in epidermal keratinocytes, exhibited impaired terminal differentiation and delayed epidermal permeability barrier (EPB) establishment during development, similar to what was observed in Ctip2 null (Ctip2(-/-)) mice. Considering that as an important role of Ctip2, and the fact that molecular networks which underlie cancer progression partially overlap with those responsible for tissue remodeling, we sought to determine the role of Ctip2 during cutaneous wound healing.
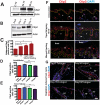
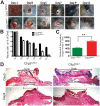
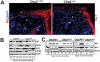
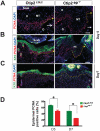
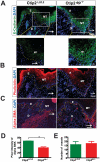
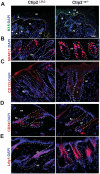
Methodology/principal findings: Full thickness excisional wound healing experiments were performed on Ctip2(L2/L2) and Ctip2(ep-/-) animals per time point and used for harvesting samples for histology, immunohistochemistry (IHC) and immunoblotting. Results demonstrated inherent defects in proliferation and migration of Ctip2 lacking keratinocytes during re-epithelialization. Mutant mice exhibited reduced epidermal proliferation, delayed keratinocyte activation, altered cell-cell adhesion and impaired ECM development. Post wounding, Ctip2(ep-/-) mice wounds displayed lack of E-Cadherin suppression in the migratory tongue, insufficient expression of alpha smooth muscle actin (alpha SMA) in the dermis, and robust induction of K8. Importantly, dysregulated expression of several hair follicle (HF) stem cell markers such as K15, NFATc1, CD133, CD34 and Lrig1 was observed in mutant skin during wound repair.
Conclusions/significance: Results confirm a cell autonomous role of keratinocytic Ctip2 to modulate cell migration, proliferation and/or differentiation, and to maintain HF stem cells during cutaneous wounding. Furthermore, Ctip2 in a non-cell autonomous manner regulated granulation tissue formation and tissue contraction during wound closure.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Transcription Factor CTIP2 Maintains Hair Follicle Stem Cell Pool and Contributes to Altered Expression of LHX2 and NFATC1.J Invest Dermatol. 2015 Nov;135(11):2593-2602. doi: 10.1038/jid.2015.281. Epub 2015 Jul 15. J Invest Dermatol. 2015. PMID: 26176759 Free PMC article.
-
Selective ablation of Ctip2/Bcl11b in epidermal keratinocytes triggers atopic dermatitis-like skin inflammatory responses in adult mice.PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e51262. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0051262. Epub 2012 Dec 20. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23284675 Free PMC article.
-
Selective Ablation of BCL11A in Epidermal Keratinocytes Alters Skin Homeostasis and Accelerates Excisional Wound Healing In Vivo.Cells. 2022 Jul 3;11(13):2106. doi: 10.3390/cells11132106. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35805190 Free PMC article.
-
CTIP2 and lipid metabolism: regulation in skin development and associated diseases.Expert Rev Proteomics. 2021 Nov;18(11):1009-1017. doi: 10.1080/14789450.2021.2003707. Epub 2021 Nov 17. Expert Rev Proteomics. 2021. PMID: 34739354 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vitamin D and calcium regulation of epidermal wound healing.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2016 Nov;164:379-385. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2015.08.011. Epub 2015 Aug 14. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 26282157 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The lysosomal trafficking regulator is necessary for normal wound healing.Wound Repair Regen. 2022 Jan;30(1):82-99. doi: 10.1111/wrr.12984. Epub 2021 Nov 27. Wound Repair Regen. 2022. PMID: 34837653 Free PMC article.
-
Cell-Cell Junctions Organize Structural and Signaling Networks.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2018 Apr 2;10(4):a029181. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a029181. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2018. PMID: 28600395 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Direct biological effects of fractional ultrapulsed CO2 laser irradiation on keratinocytes and fibroblasts in human organotypic full-thickness 3D skin models.Lasers Med Sci. 2018 May;33(4):765-772. doi: 10.1007/s10103-017-2409-1. Epub 2017 Dec 7. Lasers Med Sci. 2018. PMID: 29218493
-
Ablation of epidermal RXRα in cooperation with activated CDK4 and oncogenic NRAS generates spontaneous and acute neonatal UVB induced malignant metastatic melanomas.BMC Cancer. 2017 Nov 9;17(1):736. doi: 10.1186/s12885-017-3714-6. BMC Cancer. 2017. PMID: 29121869 Free PMC article.
-
Irx1 mechanisms for oral epithelial basal stem cell plasticity during reepithelialization after injury.JCI Insight. 2025 Jan 9;10(1):e179815. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.179815. JCI Insight. 2025. PMID: 39782692 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baranowsky A, Mokkapati S, Bechtel M, Krugel J, Miosge N, et al. Impaired wound healing in mice lacking the basement membrane protein nidogen 1. Matrix Biol. 2010;29:15–21. - PubMed
-
- Barrientos S, Stojadinovic O, Golinko MS, Brem H, Tomic-Canic M. Growth factors and cytokines in wound healing. Wound Repair Regen. 2008;16:585–601. - PubMed
-
- Gurtner GC, Werner S, Barrandon Y, Longaker MT. Wound repair and regeneration. Nature. 2008;453:314–321. - PubMed
-
- Werner S, Grose R. Regulation of wound healing by growth factors and cytokines. Physiol Rev. 2003;83:835–870. - PubMed
-
- Ito M, Liu Y, Yang Z, Nguyen J, Liang F, et al. Stem cells in the hair follicle bulge contribute to wound repair but not to homeostasis of the epidermis. Nat Med. 2005;11:1351–1354. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

