HemaMax™, a recombinant human interleukin-12, is a potent mitigator of acute radiation injury in mice and non-human primates
- PMID: 22383962
- PMCID: PMC3286478
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0030434
HemaMax™, a recombinant human interleukin-12, is a potent mitigator of acute radiation injury in mice and non-human primates
Abstract
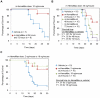
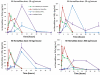
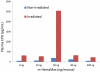
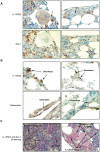
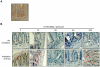
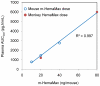
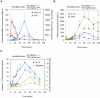
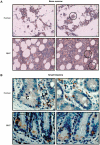
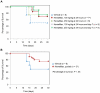
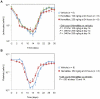
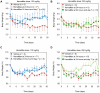
HemaMax, a recombinant human interleukin-12 (IL-12), is under development to address an unmet medical need for effective treatments against acute radiation syndrome due to radiological terrorism or accident when administered at least 24 hours after radiation exposure. This study investigated pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and efficacy of m-HemaMax (recombinant murine IL-12), and HemaMax to increase survival after total body irradiation (TBI) in mice and rhesus monkeys, respectively, with no supportive care. In mice, m-HemaMax at an optimal 20 ng/mouse dose significantly increased percent survival and survival time when administered 24 hours after TBI between 8-9 Gy (p<0.05 Pearson's chi-square test). This survival benefit was accompanied by increases in plasma interferon-γ (IFN-γ) and erythropoietin levels, recovery of femoral bone hematopoiesis characterized with the presence of IL-12 receptor β2 subunit-expressing myeloid progenitors, megakaryocytes, and osteoblasts. Mitigation of jejunal radiation damage was also examined. At allometrically equivalent doses, HemaMax showed similar pharmacokinetics in rhesus monkeys compared to m-HemaMax in mice, but more robustly increased plasma IFN-γ levels. HemaMax also increased plasma erythropoietin, IL-15, IL-18, and neopterin levels. At non-human primate doses pharmacologically equivalent to murine doses, HemaMax (100 ng/Kg and 250 ng/Kg) administered at 24 hours after TBI (6.7 Gy/LD(50/30)) significantly increased percent survival of HemaMax groups compared to vehicle (p<0.05 Pearson's chi-square test). This survival benefit was accompanied by a significantly higher leukocyte (neutrophils and lymphocytes), thrombocyte, and reticulocyte counts during nadir (days 12-14) and significantly less weight loss at day 12 compared to vehicle. These findings indicate successful interspecies dose conversion and provide proof of concept that HemaMax increases survival in irradiated rhesus monkeys by promoting hematopoiesis and recovery of immune functions and possibly gastrointestinal functions, likely through a network of interactions involving dendritic cells, osteoblasts, and soluble factors such as IL-12, IFN-γ, and cytoprotectant erythropoietin.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Therapeutic Effect of Combined Cytokines on Nonhuman Primate Model of Severe Haemopoietic Acute Radiation Sickness].Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2016 Apr;24(2):573-9. doi: 10.7534/j.issn.1009-2137.2016.02.050. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2016. PMID: 27151032 Chinese.
-
Randomized comparison of single dose of recombinant human IL-12 versus placebo for restoration of hematopoiesis and improved survival in rhesus monkeys exposed to lethal radiation.J Hematol Oncol. 2014 Apr 6;7:31. doi: 10.1186/1756-8722-7-31. J Hematol Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24708888 Free PMC article.
-
Myelopoietin, an engineered chimeric IL-3 and G-CSF receptor agonist, stimulates multilineage hematopoietic recovery in a nonhuman primate model of radiation-induced myelosuppression.Blood. 2000 Feb 1;95(3):837-45. Blood. 2000. PMID: 10648394
-
Recombinant interleukin-12, but not granulocyte-colony stimulating factor, improves survival in lethally irradiated nonhuman primates in the absence of supportive care: evidence for the development of a frontline radiation medical countermeasure.Am J Hematol. 2014 Sep;89(9):868-73. doi: 10.1002/ajh.23770. Epub 2014 Jun 19. Am J Hematol. 2014. PMID: 24852354
-
The efficacy of single-dose administration of thrombopoietin with coadministration of either granulocyte/macrophage or granulocyte colony-stimulating factor in myelosuppressed rhesus monkeys.Blood. 1997 Oct 1;90(7):2565-73. Blood. 1997. PMID: 9326222
Cited by
-
Pharmacology of natural radioprotectors.Arch Pharm Res. 2018 Nov;41(11):1033-1050. doi: 10.1007/s12272-018-1083-6. Epub 2018 Oct 25. Arch Pharm Res. 2018. PMID: 30361949 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Irradiation Haematopoiesis Recovery Orchestrated by IL-12/IL-12Rβ1/TYK2/STAT3-Initiated Osteogenic Differentiation of Mouse Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Sep 3;9:729293. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.729293. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34540843 Free PMC article.
-
Notch-Expanded Murine Hematopoietic Stem and Progenitor Cells Mitigate Death from Lethal Radiation and Convey Immune Tolerance in Mismatched Recipients.Stem Cells Transl Med. 2017 Feb;6(2):566-575. doi: 10.5966/sctm.2016-0112. Epub 2016 Sep 13. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2017. PMID: 28191773 Free PMC article.
-
Total-Body Irradiation Exacerbates Dissemination of Cutaneous Candida Albicans Infection.Radiat Res. 2016 Nov;186(5):436-446. doi: 10.1667/RR14295.1. Epub 2016 Oct 6. Radiat Res. 2016. PMID: 27710703 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-Tumor Effects after Adoptive Transfer of IL-12 Transposon-Modified Murine Splenocytes in the OT-I-Melanoma Mouse Model.PLoS One. 2015 Oct 16;10(10):e0140744. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0140744. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26473608 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Drouet M, Herodin F. Radiation victim management and the haematologist in the future: time to revisit therapeutic guidelines? Int J Radiat Biol. 2010;86:636–648. - PubMed
-
- Donnelly EH, Nemhauser JB, Smith JM, Kazzi ZN, Farfan EB, et al. Acute radiation syndrome: assessment and management. South Med J. 2010;103:541–546. - PubMed
-
- www.atomicarchive.com. Effects of radiation levels on human body. http://www.atomicarchive.com/Effects/radeffectstable.shtml. Accessed June 19, 2011.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

