Hemodialysis removes uremic toxins that alter the biological actions of endothelial cells
- PMID: 22383985
- PMCID: PMC3284471
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0030975
Hemodialysis removes uremic toxins that alter the biological actions of endothelial cells
Abstract
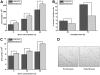
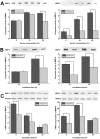
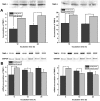
Chronic kidney disease is linked to systemic inflammation and to an increased risk of ischemic heart disease and atherosclerosis. Endothelial dysfunction associates with hypertension and vascular disease in the presence of chronic kidney disease but the mechanisms that regulate the activation of the endothelium at the early stages of the disease, before systemic inflammation is established remain obscure. In the present study we investigated the effect of serum derived from patients with chronic kidney disease either before or after hemodialysis on the activation of human endothelial cells in vitro, as an attempt to define the overall effect of uremic toxins at the early stages of endothelial dysfunction. Our results argue that uremic toxins alter the biological actions of endothelial cells and the remodelling of the extracellular matrix before signs of systemic inflammatory responses are observed. This study further elucidates the early events of endothelial dysfunction during toxic uremia conditions allowing more complete understanding of the molecular events as well as their sequence during progressive renal failure.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
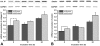
References
-
- Kitagawa S, Yamaguchi Y, Kunitomo M, Sameshima E, Fujiwara M. NG-nitro-L-arginine-resistant endothelium-dependent relaxation induced by acetylcholine in the rabbit renal artery. Life Sci. 1994;55:491–498. - PubMed
-
- Matsuda H, Hayashi K, Wakino S, Kubota E, Honda M, et al. Role of endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor in ACE inhibitor-induced renal vasodilation in vivo. Hypertension. 2004;43:603–609. - PubMed
-
- Sahin G, Yalcin AU, Akcar N. Effect of N-acetylcysteine on endothelial dysfunction in dialysis patients. Blood Purif. 2007;25:309–315. - PubMed
-
- Chappey O, Wautier MP, Wautier JL. Structure and functions of the endothelium. Rev Prat. 1997;47:2223–2226. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

