Disparate impact of butyroyloxymethyl diethylphosphate (AN-7), a histone deacetylase inhibitor, and doxorubicin in mice bearing a mammary tumor
- PMID: 22384017
- PMCID: PMC3285631
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0031393
Disparate impact of butyroyloxymethyl diethylphosphate (AN-7), a histone deacetylase inhibitor, and doxorubicin in mice bearing a mammary tumor
Abstract
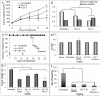
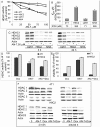
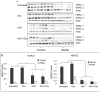
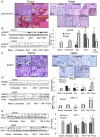
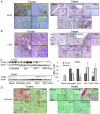
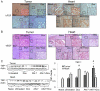
The histone deacetylase inhibitor (HDACI) butyroyloxymethyl diethylphosphate (AN-7) synergizes the cytotoxic effect of doxorubicin (Dox) and anti-HER2 on mammary carcinoma cells while protecting normal cells against their insults. This study investigated the concomitant changes occurring in heart tissue and tumors of mice bearing a subcutaneous 4T1 mammary tumor following treatment with AN-7, Dox, or their combination. Dox or AN-7 alone led to inhibition of both tumor growth and lung metastases, whereas their combination significantly increased their anticancer efficacy and attenuated Dox- toxicity. Molecular analysis revealed that treatment with Dox, AN-7, and to a greater degree, AN-7 together with Dox increased tumor levels of γH2AX, the marker for DNA double-strand breaks and decreased the expression of Rad51, a protein needed for DNA repair. These events culminated in increased apoptosis, manifested by the appearance of cytochrome-c in the cytosol. In the myocardium, Dox-induced cardiomyopathy was associated with an increase in γH2AX expression and a reduction in Rad51 and MRE11 expression and increased apoptosis. The addition of AN-7 to the Dox treatment protected the heart from Dox insults as was manifested by a decrease in γH2AX levels, an increase in Rad51 and MRE11 expression, and a diminution of cytochrome-c release. Tumor fibrosis was high in untreated mice but diminished in Dox- and AN-7-treated mice and was almost abrogated in AN-7+Dox-treated mice. By contrast, in the myocardium, Dox alone induced a dramatic increase in fibrosis, and AN7+Dox attenuated it. The high expression levels of c-Kit, Ki-67, c-Myc, lo-FGF, and VEGF in 4T1 tumors were significantly reduced by Dox or AN-7 and further attenuated by AN-7+Dox. In the myocardium, Dox suppressed these markers, whereas AN-7+Dox restored their expression. In conclusion, the combination of AN-7 and Dox results in two beneficial effects, improved anticancer efficacy and cardioprotection.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Xu WS, Parmigiani RB, Marks PA. Histone deacetylase inhibitors: molecular mechanisms of action. Oncogene. 2007;26:5541–5552. - PubMed
-
- Rosato RR, Grant S. Histone deacetylase inhibitors in clinical development. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2004;13:21–38. - PubMed
-
- Colussi C, Illi B, Rosati J, Spallotta F, Farsetti A, et al. Histone deacetylase inhibitors: Keeping momentum for neuromuscular and cardiovascular diseases treatment. Pharmacol Res. 2010;62:3–10. - PubMed
-
- Rephaeli A, Rabizadeh E, Aviram A, Shaklai M, Ruse M, et al. Derivatives of butyric acid as potential anti-neoplastic agents. Int J Cancer. 1991;49:66–72. - PubMed
-
- Rephaeli A, Blank-Porat D, Tarasenko N, Entin-Meer M, Levovich I, et al. In vivo and in vitro antitumor activity of butyroyloxymethyl-diethyl phosphate (AN-7), a histone deacetylase inhibitor, in humoan prostate cancer. Int J Cancer. 2005;116:226–235. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

