Thioredoxin glutathione reductase as a novel drug target: evidence from Schistosoma japonicum
- PMID: 22384025
- PMCID: PMC3285170
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0031456
Thioredoxin glutathione reductase as a novel drug target: evidence from Schistosoma japonicum
Abstract
Background: Schistosomiasis remains a major public health concern affecting billions of people around the world. Currently, praziquantel is the only drug of choice for treatment of human schistosomiasis. The emergence of drug resistance to praziquantel in schistosomes makes the development of novel drugs an urgent task. Thioredoxin glutathione reductase (TGR) enzymes in Schistosoma mansoni and some other platyhelminths have been identified as alternative targets. The present study was designed to confirm the existense and the potential value of TGR as a target for development of novel antischistosomal agents in Schistosoma japonicum, a platyhelminth endemic in Asia.
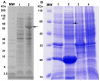
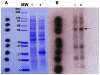
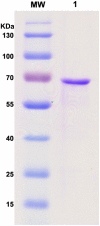
Methods and findings: After cloning the S. japonicum TGR (SjTGR) gene, the recombinant SjTGR selenoprotein was purified and characterized in enzymatic assays as a multifunctional enzyme with thioredoxin reductase (TrxR), glutathione reductase (GR) and glutaredoxin (Grx) activities. Immunological and bioinformatic analyses confirmed that instead of having separate TrxR and GR proteins in mammalian, S. japonicum only encodes TGR, which performs the functions of both enzymes and plays a critical role in maintaining the redox balance in this parasite. These results were in good agreement with previous findings in Schistosoma mansoni and some other platyhelminths. Auranofin, a known inhibitor against TGR, caused fatal toxicity in S. japonicum adult worms in vitro and reduced worm and egg burdens in S. japonicum infected mice.
Conclusions: Collectively, our study confirms that a multifunctional enzyme SjTGR selenoprotein, instead of separate TrxR and GR enzymes, exists in S. japonicum. Furthermore, TGR may be a potential target for development of novel agents against schistosomes. This assumption is strengthened by our demonstration that the SjTGR is an essential enzyme for maintaining the thiol-disulfide redox homeostasis of S. japonicum.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
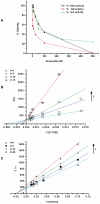
 ) values of auranofin on recombinant SjTGR in the TrxR assay. The straight lines were fitted on the basis of the reciprocal of concentration of substrate and initial velocity. The concentrations of auranofin were 0 nM, 5 nM, 10 nM and 15 nM, and DTNB ranged from 60 to 1,000 µM. (C) Inhibition constant (
) values of auranofin on recombinant SjTGR in the TrxR assay. The straight lines were fitted on the basis of the reciprocal of concentration of substrate and initial velocity. The concentrations of auranofin were 0 nM, 5 nM, 10 nM and 15 nM, and DTNB ranged from 60 to 1,000 µM. (C) Inhibition constant ( ) values of auranofin on SjTGR in the GR activity assay. The straight lines were fitted on the basis of the reciprocal of concentration of substrate and initial velocity. The concentrations of auranofin were 0 nM, 5 nM, 10 nM and 20 nM, and GSSG ranged from 10 to 100 µM.
) values of auranofin on SjTGR in the GR activity assay. The straight lines were fitted on the basis of the reciprocal of concentration of substrate and initial velocity. The concentrations of auranofin were 0 nM, 5 nM, 10 nM and 20 nM, and GSSG ranged from 10 to 100 µM.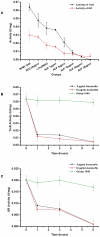
References
-
- Steinmann P, Keiser J, Bos R, Tanner M, Utzinger J. Schistosomiasis and water resources development, systematic review, meta-analysis, and estimates of people at risk. Lancet Infect Dis. 2006;6:411–25. - PubMed
-
- Van der Werf MJ, de Vlas SJ, Brooker S, Looman CW, Nagelkerke NJ, et al. Quantification of clinical morbidity associated with schistosome infection in sub-Saharan Africa. Acta Trop. 2003;86:125–139. - PubMed
-
- King CH, Dickman K, Tisch DJ. Reassessment of the cost of chronic helminth infection: a meta-analysis of disability-related outcomes in endemic schistosomiasis. Lancet. 2005;365:1561–1569. - PubMed
-
- Hao Y, Zheng H, Zhu R, Guo JG, Wang LY, et al. Schistosomiasis situation in People's Republic of China in 2009. Chin J Schisto Control. 2010;22:521–527.
-
- Cioli D, Pica-Mattoccia L, Archer S. Antischistosomal drugs: past, present and future? Pharmacol Ther. 1995;68:35–85. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

