Reconstruction of hematopoietic inductive microenvironment after transplantation of VCAM-1-modified human umbilical cord blood stromal cells
- PMID: 22384064
- PMCID: PMC3285638
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0031741
Reconstruction of hematopoietic inductive microenvironment after transplantation of VCAM-1-modified human umbilical cord blood stromal cells
Abstract
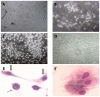
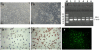
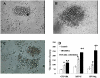
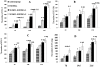
The hematopoietic inductive microenvironment (HIM) is where hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells grow and develop. Hematopoietic stromal cells were the key components of the HIM. In our previous study, we had successfully cultured and isolated human cord blood-derived stromal cells (HUCBSCs) and demonstrated that they could secret hemopoietic growth factors such as GM-CSF, TPO, and SCF. However, it is still controversial whether HUCBSCs can be used for reconstruction of HIM. In this study, we first established a co-culture system of HUCBSCs and cord blood CD34(+) cells and then determined that using HUCBSCs as the adherent layer had significantly more newly formed colonies of each hematopoietic lineage than the control group, indicating that HUCBSCs had the ability to promote the proliferation of hematopoietic stem cells/progenitor cells. Furthermore, the number of colonies was significantly higher in vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1)-modified HUCBSCs, suggesting that the ability of HUCBSCs in promoting the proliferation of hematopoietic stem cells/progenitor cells was further enhanced after having been modified with VCAM-1. Next, HUCBSCs were infused into a radiation-damaged animal model, in which the recovery of hematopoiesis was observed. The results demonstrate that the transplanted HUCBSCs were "homed in" to bone marrow and played roles in promoting the recovery of irradiation-induced hematopoietic damage and repairing HIM. Compared with the control group, the HUCBSC group had significantly superior effectiveness in terms of the recovery time for hemogram and myelogram, CFU-F, CFU-GM, BFU-E, and CFU-Meg. Such differences were even more significant in VCAM-1-modified HUCBSCs group. We suggest that HUCBSCs are able to restore the functions of HIM and promote the recovery of radiation-induced hematopoietic damage. VCAM-1 plays an important role in supporting the repair of HIM damage.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





References
-
- Fukushima N, Ohkawa H. Hematopoietic stem cells and microenvironment: the proliferation and differentiation of stromal cells. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 1995;20:255–270. - PubMed
-
- Lo Celso C, Wu JW, Lin CP. In vivo imaging of hematopoietic stem cells and their microenvironment. J Biophotonics. 2009;2:619–631. - PubMed
-
- O'Flaherty E, Sparrow R, Szer J. Bone marrow stromal function from patients after bone marrow transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1995;15:207–212. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

