G Protein βγ-subunit signaling mediates airway hyperresponsiveness and inflammation in allergic asthma
- PMID: 22384144
- PMCID: PMC3284547
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0032078
G Protein βγ-subunit signaling mediates airway hyperresponsiveness and inflammation in allergic asthma
Abstract
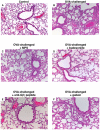
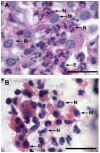
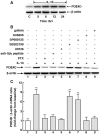
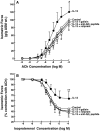
Since the Gβγ subunit of Gi protein has been importantly implicated in regulating immune and inflammatory responses, this study investigated the potential role and mechanism of action of Gβγ signaling in regulating the induction of airway hyperresponsiveness (AHR) in a rabbit model of allergic asthma. Relative to non-sensitized animals, OVA-sensitized rabbits challenged with inhaled OVA exhibited AHR, lung inflammation, elevated BAL levels of IL-13, and increased airway phosphodiesterase-4 (PDE4) activity. These proasthmatic responses were suppressed by pretreatment with an inhaled membrane-permeable anti-Gβγ blocking peptide, similar to the suppressive effect of glucocorticoid pretreatment. Extended mechanistic studies demonstrated that: 1) corresponding proasthmatic changes in contractility exhibited in isolated airway smooth muscle (ASM) sensitized with serum from OVA-sensitized+challenged rabbits or IL-13 were also Gβγ-dependent and mediated by MAPK-upregulated PDE4 activity; and 2) the latter was attributed to Gβγ-induced direct stimulation of the non-receptor tyrosine kinase, c-Src, resulting in downstream activation of ERK1/2 and its consequent transcriptional upregulation of PDE4. Collectively, these data are the first to identify that a mechanism involving Gβγ-induced direct activation of c-Src, leading to ERK1/2-mediated upregulation of PDE4 activity, plays a decisive role in regulating the induction of AHR and inflammation in a rabbit model of allergic airway disease.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





Similar articles
-
Constitutively active signaling by the G protein βγ-subunit mediates intrinsically increased phosphodiesterase-4 activity in human asthmatic airway smooth muscle cells.PLoS One. 2015 Mar 5;10(3):e0118712. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0118712. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25742624 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism regulating proasthmatic effects of prolonged homologous beta2-adrenergic receptor desensitization in airway smooth muscle.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2009 Oct;297(4):L746-57. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00079.2009. Epub 2009 Aug 7. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19666775 Free PMC article.
-
Prolonged heterologous beta2-adrenoceptor desensitization promotes proasthmatic airway smooth muscle function via PKA/ERK1/2-mediated phosphodiesterase-4 induction.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2008 Jun;294(6):L1055-67. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00021.2008. Epub 2008 Mar 21. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18359889
-
Role of IgE in the development of allergic airway inflammation and airway hyperresponsiveness--a murine model.Allergy. 1999 Apr;54(4):297-305. doi: 10.1034/j.1398-9995.1999.00085.x. Allergy. 1999. PMID: 10371087 Review.
-
RhoA, a possible target for treatment of airway hyperresponsiveness in bronchial asthma.J Pharmacol Sci. 2010;114(3):239-47. doi: 10.1254/jphs.10r03cr. Epub 2010 Oct 8. J Pharmacol Sci. 2010. PMID: 20948164 Review.
Cited by
-
Constitutively active signaling by the G protein βγ-subunit mediates intrinsically increased phosphodiesterase-4 activity in human asthmatic airway smooth muscle cells.PLoS One. 2015 Mar 5;10(3):e0118712. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0118712. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25742624 Free PMC article.
-
Salmeterol Efficacy and Bias in the Activation and Kinase-Mediated Desensitization of β2-Adrenergic Receptors.Mol Pharmacol. 2015 Jun;87(6):954-64. doi: 10.1124/mol.114.096800. Epub 2015 Mar 17. Mol Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25784721 Free PMC article.
-
Asthma: The Use of Animal Models and Their Translational Utility.Cells. 2023 Apr 5;12(7):1091. doi: 10.3390/cells12071091. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37048164 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Homeostatic glucocorticoid signaling in airway smooth muscle: A roadmap to asthma pathogenesis.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Jan 4;13:1077389. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1077389. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 36686425 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of Gαi activity by Gβγ is mediated by PI 3-kinase-γ- and cSrc-dependent tyrosine phosphorylation of Gαi and recruitment of RGS12.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2014 May 1;306(9):G802-10. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00440.2013. Epub 2014 Feb 27. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24578342 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hepler JR, Gilman AG. G proteins. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992;17:383–387. - PubMed
-
- Goldsmith ZB, Dhanasekaran DN. G protein regulation of MAPK networks. Oncogene. 2007;26:3122–3142. - PubMed
-
- Gerthoffer WT, Singer CA. MAPK regulation of gene expression in airway smooth muscle. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2003;137:237–250. - PubMed
-
- Hakonarson H, Grunstein MM. Autocrine regulation of airway smooth muscle responsiveness. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2003;137:263–276. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

