Interaction between M-like protein and macrophage thioredoxin facilitates antiphagocytosis for Streptococcus equi ssp. zooepidemicus
- PMID: 22384152
- PMCID: PMC3288065
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0032099
Interaction between M-like protein and macrophage thioredoxin facilitates antiphagocytosis for Streptococcus equi ssp. zooepidemicus
Erratum in
- PLoS One. 2012;7(5): doi/10.1371/annotation/a1d856e3-285c-4728-b817-c030fb5ec20b
Abstract
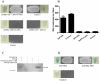
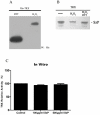
Streptococcus equi ssp. zooepidemicus (S. zooepidemicus, S.z) is one of the common pathogens that can cause septicemia, meningitis, and mammitis in domesticated species. M-like protein (SzP) is an important virulence factor of S. zooepidemicus and contributes to bacterial infection and antiphagocytosis. The interaction between SzP of S. zooepidemicus and porcine thioredoxin (TRX) was identified by the yeast two-hybrid and further confirmed by co-immunoprecipitation. SzP interacted with both reduced and the oxidized forms of TRX without inhibiting TRX activity. Membrane anchored SzP was able to recruit TRX to the surface, which would facilitate the antiphagocytosis of the bacteria. Further experiments revealed that TRX regulated the alternative complement pathway by inhibiting C3 convertase activity and associating with factor H (FH). TRX alone inhibited C3 cleavage and C3a production, and the inhibitory effect was additive when FH was also present. TRX inhibited C3 deposition on the bacterial surface when it was recruited by SzP. These new findings indicated that S. zooepidemicus used SzP to recruit TRX and regulated the alternative complement pathways to evade the host immune phagocytosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
-
- Eyre DW, J SK, Bowler IC, McBride SJ. Streptococcus equi subspecies zooepidemicus meningitis-a case report and review of the literature. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 2010 - PubMed
-
- Abbott Y, Acke E, Khan S, Muldoon E, Markey B, et al. Zoonotic transmission of Streptococcus equi subsp. zooepidemicus from a dog to a handler. J Med Microbiol 2009 - PubMed
-
- Hornef MW, Wick MJ, Rhen M, Normark S. Bacterial strategies for overcoming host innate and adaptive immune responses. Nat Immunol. 2002;3:1033–1040. - PubMed
-
- Ernst JD. Bacterial inhibition of phagocytosis. Cell Microbiol. 2000;2:379–386. - PubMed
-
- Wibawan IW, Pasaribu FH, Utama IH, Abdulmawjood A, Lammler C. The role of hyaluronic acid capsular material of Streptococcus equi subsp. zooepidemicus in mediating adherence to HeLa cells and in resisting phagocytosis. Res Vet Sci. 1999;67:131–135. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

