FoxO1 gain of function in the pancreas causes glucose intolerance, polycystic pancreas, and islet hypervascularization
- PMID: 22384192
- PMCID: PMC3285669
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0032249
FoxO1 gain of function in the pancreas causes glucose intolerance, polycystic pancreas, and islet hypervascularization
Abstract
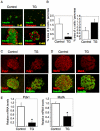
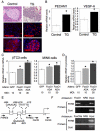
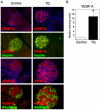
Genetic studies revealed that the ablation of insulin/IGF-1 signaling in the pancreas causes diabetes. FoxO1 is a downstream transcription factor of insulin/IGF-1 signaling. We previously reported that FoxO1 haploinsufficiency restored β cell mass and rescued diabetes in IRS2 knockout mice. However, it is still unclear whether FoxO1 dysregulation in the pancreas could be the cause of diabetes. To test this hypothesis, we generated transgenic mice overexpressing constitutively active FoxO1 specifically in the pancreas (TG). TG mice had impaired glucose tolerance and some of them indeed developed diabetes due to the reduction of β cell mass, which is associated with decreased Pdx1 and MafA in β cells. We also observed increased proliferation of pancreatic duct epithelial cells in TG mice and some mice developed a polycystic pancreas as they aged. Furthermore, TG mice exhibited islet hypervascularities due to increased VEGF-A expression in β cells. We found FoxO1 binds to the VEGF-A promoter and regulates VEGF-A transcription in β cells. We propose that dysregulation of FoxO1 activity in the pancreas could account for the development of diabetes and pancreatic cysts.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Kulkarni RN, Bruning JC, Winnay JN, Postic C, Magnuson MA, et al. Tissue-specific knockout of the insulin receptor in pancreatic beta cells creates an insulin secretory defect similar to that in type 2 diabetes. Cell. 1999;96:329–339. - PubMed
-
- Ueki K, Okada T, Hu J, Liew CW, Assmann A, et al. Total insulin and IGF-I resistance in pancreatic beta cells causes overt diabetes. Nat Genet. 2006;38:583–588. - PubMed
-
- Withers DJ, Sanchez-Gutierrez J, Towery H, Burks DJ, Ren J-M, et al. Disruption of IRS-2 causes type 2 diabetes in mice. Nature. 1998;391:900–904. - PubMed
-
- Kubota N, Tobe K, Terauchi Y, Eto K, Yamauchi T, et al. Disruption of insulin receptor substrate 2 causes type 2 diabetes because of liver insulin resistance and lack of compensatory beta-cell hyperplasia. Diabetes. 2000;49:1880–1889. - PubMed
-
- Hashimoto N, Kido Y, Uchida T, Asahara S, Shigeyama Y, et al. Ablation of PDK1 in pancreatic beta cells induces diabetes as a result of loss of beta cell mass. Nat Genet. 2006;38:589–593. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

