Platelet-associated CD40/CD154 mediates remote tissue damage after mesenteric ischemia/reperfusion injury
- PMID: 22384195
- PMCID: PMC3288090
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0032260
Platelet-associated CD40/CD154 mediates remote tissue damage after mesenteric ischemia/reperfusion injury
Abstract
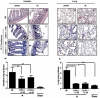
Several innate and adaptive immune cell types participate in ischemia/reperfusion induced tissue injury. Amongst them, platelets have received little attention as contributors in the process of tissue damage after ischemia reperfusion (I/R) injury. It is currently unknown whether platelets participate through the immunologically important molecules including, CD40 and when activated, CD154 (CD40L), in the pathogenesis of I/R injury. We hypothesized that constitutive expression of CD40 and activation-induced expression of CD154 on platelets mediate local mesenteric and remote lung tissue damage after I/R injury. Wild type (WT; C57BL/6J), CD40 and CD154 deficient mice underwent mesenteric ischemia for 30 minutes followed by reperfusion for 3 hours. WT mice subjected to mesenteric I/R injury displayed both local intestinal and remote lung damage. In contrast, there was significantly less intestinal damage and no remote lung injury in CD40 and CD154 deficient mice when compared to WT mice. Platelet-depleted WT mice transfused with platelets from CD40 or CD154 deficient mice failed to reconstitute remote lung damage. In contrast, when CD40 or CD154 deficient mice were transfused with WT platelets lung tissue damage was re-established. Together, these findings suggest that multiple mechanisms are involved in local and remote tissue injury and also identify platelet-expressed CD40 and/or CD154 as mediators of remote tissue damage.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
Platelets orchestrate remote tissue damage after mesenteric ischemia-reperfusion.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2012 Apr 15;302(8):G888-97. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00499.2011. Epub 2012 Feb 2. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22301111
-
Inhibition of Syk activity by R788 in platelets prevents remote lung tissue damage after mesenteric ischemia-reperfusion injury.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2012 Jun 15;302(12):G1416-22. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00026.2012. Epub 2012 Apr 5. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22492694
-
CD154-CD40 T-cell costimulation pathway is required in the mechanism of hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury, and its blockade facilitates and depends on heme oxygenase-1 mediated cytoprotection.Transplantation. 2002 Aug 15;74(3):315-9. doi: 10.1097/00007890-200208150-00005. Transplantation. 2002. PMID: 12177608
-
Targeting the CD40-CD154 Signaling Pathway for Treatment of Autoimmune Arthritis.Cells. 2019 Aug 18;8(8):927. doi: 10.3390/cells8080927. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31426619 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Platelet-associated CD154: a new interface in haemostasis and in the inflammatory reaction].Med Sci (Paris). 2005 Oct;21(10):825-31. doi: 10.1051/medsci/20052110825. Med Sci (Paris). 2005. PMID: 16197899 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Advances in research on the effects of platelet activation in acute lung injury (Review).Biomed Rep. 2022 Mar;16(3):17. doi: 10.3892/br.2022.1500. Epub 2022 Jan 19. Biomed Rep. 2022. PMID: 35154701 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tumor Necrosis Factor-α: Life and Death of Hepatocytes During Liver Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury.Ochsner J. 2013 Spring;13(1):119-30. Ochsner J. 2013. PMID: 23531747 Free PMC article.
-
New frontiers for platelet CD154.Exp Hematol Oncol. 2015 Mar 1;4:6. doi: 10.1186/s40164-015-0001-6. eCollection 2015. Exp Hematol Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25763299 Free PMC article.
-
Activated platelets and platelet-leukocyte aggregates in the equine systemic inflammatory response syndrome.J Vet Diagn Invest. 2022 May;34(3):448-457. doi: 10.1177/10406387221077969. Epub 2022 Feb 15. J Vet Diagn Invest. 2022. PMID: 35168432 Free PMC article.
-
The Inhibition of CD40/CD154 Costimulatory Signaling in the Prevention of Renal Transplant Rejection in Nonhuman Primates: A Systematic Review and Meta Analysis.Front Immunol. 2022 Apr 7;13:861471. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.861471. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35464470 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Diepenhorst GM, van Gulik TM, Hack CE. Complement-mediated ischemia-reperfusion injury: lessons learned from animal and clinical studies. Ann Surg. 2009;249:889–899. - PubMed
-
- Williams JP, Pechet TT, Weiser MR, Reid R, Kobzik L, et al. Intestinal reperfusion injury is mediated by IgM and complement. J Appl Physiol. 1999;86:938–942. - PubMed
-
- Fleming SD, Anderson J, Wilson F, Shea-Donohue T, Tsokos GC. C5 is required for CD49d expression on neutrophils and VCAM expression on vascular endothelial cells following mesenteric ischemia/reperfusion. Clin Immunol. 2003;106:55–64. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

