Cytokine signaling in splenic leukocytes from vaccinated and non-vaccinated chickens after intravenous infection with Salmonella enteritidis
- PMID: 22384225
- PMCID: PMC3286471
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0032346
Cytokine signaling in splenic leukocytes from vaccinated and non-vaccinated chickens after intravenous infection with Salmonella enteritidis
Abstract
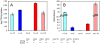
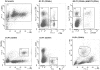
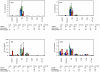
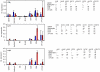
In order to design a new Salmonella enterica vaccine, one needs to understand how naive and immune chickens interact differently when exposed to S. enterica. In this study we therefore determined the immune response of vaccinated and non-vaccinated chickens after intravenous infection with Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis (S. Enteritidis). Using flow cytometry we showed that 4 days post infection (DPI), counts of CD4 and B-lymphocytes did not change, CD8 and γδ T-lymphocytes decreased and macrophages and heterophils increased in the spleen. When vaccinated and non-vaccinated chickens were compared, only macrophages and heterophils were found in significantly higher counts in the spleens of the non-vaccinated chickens. The non-vaccinated chickens also expressed higher anti-LPS antibodies than the vaccinated chickens. The expression of interleukin (IL)1β, IL6, IL8, IL18, LITAF, IFNγ and iNOS did not exhibit any clear pattern in the cells sorted from the spleens of vaccinated or non-vaccinated chickens. Only IL17 and IL22 showed a differential expression in the CD4 T-lymphocytes of the vaccinated and non-vaccinated chickens at 4 DPI, both being expressed at a higher level in the non-vaccinated chickens. Due to a similar IFNγ expression in the CD4 T-lymphocytes in both the vaccinated and non-vaccinated chickens, and a variable IL17 expression oscillating around IFNγ expression levels, the IL17∶IFNγ ratio in CD4 T-lymphocytes was found to be central for the outcome of the immune response. When IL17 was expressed at higher levels than IFNγ in the non-vaccinated chickens, the Th17 immune response with a higher macrophage and heterophil infiltration in the spleen dominated. However, when the expression of IL17 was lower than that of IFNγ as in the vaccinated chickens, the Th1 response with a higher resistance to S. Enteritidis infection dominated.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

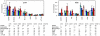
Similar articles
-
Gene expression in the chicken caecum in response to infections with non-typhoid Salmonella.Vet Res. 2014 Dec 5;45(1):119. doi: 10.1186/s13567-014-0119-2. Vet Res. 2014. PMID: 25475706 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunological changes at point-of-lay increase susceptibility to Salmonella enterica Serovar enteritidis infection in vaccinated chickens.PLoS One. 2012;7(10):e48195. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0048195. Epub 2012 Oct 25. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23133568 Free PMC article.
-
Different roles of CD4, CD8 and γδ T-lymphocytes in naive and vaccinated chickens during Salmonella Enteritidis infection.Proteomics. 2017 Jul;17(13-14). doi: 10.1002/pmic.201700073. Proteomics. 2017. PMID: 28621911
-
Effects of Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis on cellular recruitment and cytokine gene expression in caecum of vaccinated chickens.Vaccine. 2008 Oct 3;26(42):5423-33. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2008.07.088. Epub 2008 Aug 14. Vaccine. 2008. PMID: 18706948
-
Cell-mediated immune responses to a killed Salmonella enteritidis vaccine: lymphocyte proliferation, T-cell changes and interleukin-6 (IL-6), IL-1, IL-2, and IFN-gamma production.Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis. 2004 Jul;27(4):255-72. doi: 10.1016/j.cimid.2003.12.001. Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis. 2004. PMID: 15178000
Cited by
-
phoP, SPI1, SPI2 and aroA mutants of Salmonella Enteritidis induce a different immune response in chickens.Vet Res. 2015 Sep 17;46(1):96. doi: 10.1186/s13567-015-0224-x. Vet Res. 2015. PMID: 26380970 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin 4 inducible 1 gene (IL4I1) is induced in chicken phagocytes by Salmonella Enteritidis infection.Vet Res. 2020 May 13;51(1):67. doi: 10.1186/s13567-020-00792-y. Vet Res. 2020. PMID: 32404145 Free PMC article.
-
Gene expression in the chicken caecum in response to infections with non-typhoid Salmonella.Vet Res. 2014 Dec 5;45(1):119. doi: 10.1186/s13567-014-0119-2. Vet Res. 2014. PMID: 25475706 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunization of Broiler Chickens With a Killed Chitosan Nanoparticle Salmonella Vaccine Decreases Salmonella Enterica Serovar Enteritidis Load.Front Physiol. 2022 Jul 18;13:920777. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.920777. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35923229 Free PMC article.
-
Differential protein expression in chicken macrophages and heterophils in vivo following infection with Salmonella Enteritidis.Vet Res. 2017 Jun 17;48(1):35. doi: 10.1186/s13567-017-0439-0. Vet Res. 2017. PMID: 28623956 Free PMC article.
References
-
- van Dijk A, Tersteeg-Zijderveld MH, Tjeerdsma-van Bokhoven JL, Jansman AJ, Veldhuizen EJ, et al. Chicken heterophils are recruited to the site of Salmonella infection and release antibacterial mature cathelicidin-2 upon stimulation with LPS. Mol Immunol. 2009;46:1517–26. - PubMed
-
- Berndt A, Methner U. Gamma/delta T cell response of chickens after oral administration of attenuated and non-attenuated Salmonella typhimurium strains. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2001;78:143–61. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

