Spleen tyrosine kinase regulates AP-1 dependent transcriptional response to minimally oxidized LDL
- PMID: 22384232
- PMCID: PMC3284564
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0032378
Spleen tyrosine kinase regulates AP-1 dependent transcriptional response to minimally oxidized LDL
Abstract
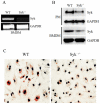
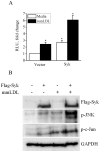
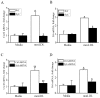
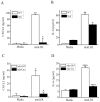
Oxidative modification of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) turns it into an endogenous ligand recognized by pattern-recognition receptors. We have demonstrated that minimally oxidized LDL (mmLDL) binds to CD14 and mediates TLR4/MD-2-dependent responses in macrophages, many of which are MyD88-independent. We have also demonstrated that the mmLDL activation leads to recruitment of spleen tyrosine kinase (Syk) to TLR4 and TLR4 and Syk phosphorylation. In this study, we produced a macrophage-specific Syk knockout mouse and used primary Syk(-/-) macrophages in our studies. We demonstrated that Syk mediated phosphorylation of ERK1/2 and JNK, which in turn phosphorylated c-Fos and c-Jun, respectively, as assessed by an in vitro kinase assay. c-Jun phosphorylation was also mediated by IKKε. c-Jun and c-Fos bound to consensus DNA sites and thereby completed an AP-1 transcriptional complex and induced expression of CXCL2 and IL-6. These results suggest that Syk plays a key role in TLR4-mediated macrophage responses to host-generated ligands, like mmLDL, with subsequent activation of an AP-1 transcription program.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Jakus Z, Fodor S, Abram CL, Lowell CA, Mocsai A. Immunoreceptor-like signaling by [beta]2 and [beta]3 integrins. Trends in Cell Biology. 2007;17:493–501. - PubMed
-
- Woodside DG, Obergfell A, Talapatra A, Calderwood DA, Shattil SJ, et al. The N-terminal SH2 Domains of Syk and ZAP-70 Mediate Phosphotyrosine-independent Binding to Integrin Cytoplasmic Domains. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:39401–39408. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

