Conditionally immortalized mouse embryonic fibroblasts retain proliferative activity without compromising multipotent differentiation potential
- PMID: 22384246
- PMCID: PMC3285668
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0032428
Conditionally immortalized mouse embryonic fibroblasts retain proliferative activity without compromising multipotent differentiation potential
Erratum in
- PLoS One. 2013;8(1). doi: 10.1371/annotation/2f1c6442-0ecb-4a33-9534-aae89b5fbbc1
Abstract
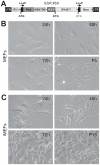
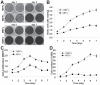
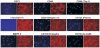
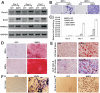
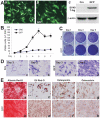
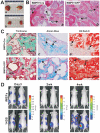
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are multipotent cells which reside in many tissues and can give rise to multiple lineages including bone, cartilage and adipose. Although MSCs have attracted significant attention for basic and translational research, primary MSCs have limited life span in culture which hampers MSCs' broader applications. Here, we investigate if mouse mesenchymal progenitors can be conditionally immortalized with SV40 large T antigen and maintain long-term cell proliferation without compromising their multipotency. Using the system which expresses SV40 large T antigen flanked with Cre/loxP sites, we demonstrate that mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) can be efficiently immortalized by SV40 large T antigen. The conditionally immortalized MEFs (iMEFs) exhibit an enhanced proliferative activity and maintain long-term cell proliferation, which can be reversed by Cre recombinase. The iMEFs express most MSC markers and retain multipotency as they can differentiate into osteogenic, chondrogenic and adipogenic lineages under appropriate differentiation conditions in vitro and in vivo. The removal of SV40 large T reduces the differentiation potential of iMEFs possibly due to the decreased progenitor expansion. Furthermore, the iMEFs are apparently not tumorigenic when they are subcutaneously injected into athymic nude mice. Thus, the conditionally immortalized iMEFs not only maintain long-term cell proliferation but also retain the ability to differentiate into multiple lineages. Our results suggest that the reversible immortalization strategy using SV40 large T antigen may be an efficient and safe approach to establishing long-term cell culture of primary mesenchymal progenitors for basic and translational research, as well as for potential clinical applications.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
The piggyBac transposon-mediated expression of SV40 T antigen efficiently immortalizes mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs).PLoS One. 2014 May 20;9(5):e97316. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0097316. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24845466 Free PMC article.
-
Reversibly immortalized human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells (UC-MSCs) are responsive to BMP9-induced osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation.J Cell Biochem. 2018 Nov;119(11):8872-8886. doi: 10.1002/jcb.27140. Epub 2018 Aug 4. J Cell Biochem. 2018. PMID: 30076626 Free PMC article.
-
Establishment and characterization of the reversibly immortalized mouse fetal heart progenitors.Int J Med Sci. 2013 Jun 20;10(8):1035-46. doi: 10.7150/ijms.6639. Print 2013. Int J Med Sci. 2013. PMID: 23801891 Free PMC article.
-
Immortalization of hepatic progenitor cells.Pathol Biol (Paris). 2004 Mar;52(2):93-6. doi: 10.1016/j.patbio.2003.02.001. Pathol Biol (Paris). 2004. PMID: 15001238 Review.
-
Immortalization of neuronal progenitors using SV40 large T antigen and differentiation towards dopaminergic neurons.J Cell Mol Med. 2012 Nov;16(11):2592-610. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2012.01607.x. J Cell Mol Med. 2012. PMID: 22863662 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Decellularized liver scaffolds effectively support the proliferation and differentiation of mouse fetal hepatic progenitors.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2014 Apr;102(4):1017-25. doi: 10.1002/jbm.a.34764. Epub 2013 Jun 4. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2014. PMID: 23625886 Free PMC article.
-
Monensin inhibits cell proliferation and tumor growth of chemo-resistant pancreatic cancer cells by targeting the EGFR signaling pathway.Sci Rep. 2018 Dec 17;8(1):17914. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-36214-5. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30559409 Free PMC article.
-
lncRNA Rmst acts as an important mediator of BMP9-induced osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) by antagonizing Notch-targeting microRNAs.Aging (Albany NY). 2019 Dec 11;11(24):12476-12496. doi: 10.18632/aging.102583. Epub 2019 Dec 11. Aging (Albany NY). 2019. PMID: 31825894 Free PMC article.
-
Recombinant adenovirus (AdEasy system) mediated exogenous expression of long non-coding RNA H19 (lncRNA H19) biphasic regulating osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs).Am J Transl Res. 2020 May 15;12(5):1700-1713. eCollection 2020. Am J Transl Res. 2020. PMID: 32509170 Free PMC article.
-
Bone morphogenetic protein-9 effectively induces osteo/odontoblastic differentiation of the reversibly immortalized stem cells of dental apical papilla.Stem Cells Dev. 2014 Jun 15;23(12):1405-16. doi: 10.1089/scd.2013.0580. Epub 2014 Mar 21. Stem Cells Dev. 2014. PMID: 24517722 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Prockop DJ. Marrow stromal cells as stem cells for nonhematopoietic tissues. Science. 1997;276:71–74. - PubMed
-
- Pittenger MF, Mackay AM, Beck SC, Jaiswal RK, Douglas R, et al. Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells. Science. 1999;284:143–147. - PubMed
-
- Caplan AI, Bruder SP. Mesenchymal stem cells: building blocks for molecular medicine in the 21st century. Trends in Mol Med. 2001;7:259–264. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

