Sequence Analysis of the Segmental Duplication Responsible for Paris Sex-Ratio Drive in Drosophila simulans
- PMID: 22384350
- PMCID: PMC3276153
- DOI: 10.1534/g3.111.000315
Sequence Analysis of the Segmental Duplication Responsible for Paris Sex-Ratio Drive in Drosophila simulans
Abstract
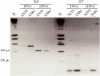
Sex-ratio distorters are X-linked selfish genetic elements that facilitate their own transmission by subverting Mendelian segregation at the expense of the Y chromosome. Naturally occurring cases of sex-linked distorters have been reported in a variety of organisms, including several species of Drosophila; they trigger genetic conflict over the sex ratio, which is an important evolutionary force. However, with a few exceptions, the causal loci are unknown. Here, we molecularly characterize the segmental duplication involved in the Paris sex-ratio system that is still evolving in natural populations of Drosophila simulans. This 37.5 kb tandem duplication spans six genes, from the second intron of the Trf2 gene (TATA box binding protein-related factor 2) to the first intron of the org-1 gene (optomotor-blind-related-gene-1). Sequence analysis showed that the duplication arose through the production of an exact copy on the template chromosome itself. We estimated this event to be less than 500 years old. We also detected specific signatures of the duplication mechanism; these support the Duplication-Dependent Strand Annealing model. The region at the junction between the two duplicated segments contains several copies of an active transposable element, Hosim1, alternating with 687 bp repeats that are noncoding but transcribed. The almost-complete sequence identity between copies made it impossible to complete the sequencing and assembly of this region. These results form the basis for the functional dissection of Paris sex-ratio drive and will be valuable for future studies designed to better understand the dynamics and the evolutionary significance of sex chromosome drive.
Keywords: D. simulans; meiotic drive; segmental duplication; sex-ratio.
Figures



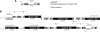
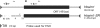
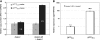

Similar articles
-
Local dynamics of a fast-evolving sex-ratio system in Drosophila simulans.Mol Ecol. 2013 Nov;22(21):5352-67. doi: 10.1111/mec.12492. Epub 2013 Oct 5. Mol Ecol. 2013. PMID: 24118375
-
The fate of a suppressed X-linked meiotic driver: experimental evolution in Drosophila simulans.Chromosome Res. 2022 Sep;30(2-3):141-150. doi: 10.1007/s10577-022-09698-1. Epub 2022 May 30. Chromosome Res. 2022. PMID: 35635636
-
Sex-ratio meiotic drive in Drosophila simulans: cellular mechanism, candidate genes and evolution.Biochem Soc Trans. 2006 Aug;34(Pt 4):562-5. doi: 10.1042/BST0340562. Biochem Soc Trans. 2006. PMID: 16856861 Review.
-
Rapid rise and fall of selfish sex-ratio X chromosomes in Drosophila simulans: spatiotemporal analysis of phenotypic and molecular data.Mol Biol Evol. 2011 Sep;28(9):2461-70. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msr074. Epub 2011 Apr 15. Mol Biol Evol. 2011. PMID: 21498605
-
The selfish Segregation Distorter gene complex of Drosophila melanogaster.Genetics. 2012 Sep;192(1):33-53. doi: 10.1534/genetics.112.141390. Genetics. 2012. PMID: 22964836 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Contrasting patterns of X-chromosome divergence underlie multiple sex-ratio polymorphisms in stalk-eyed flies.J Evol Biol. 2017 Sep;30(9):1772-1784. doi: 10.1111/jeb.13140. Epub 2017 Aug 4. J Evol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28688201 Free PMC article.
-
Out with the old, in with the new: Meiotic driving of sex chromosome evolution.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Nov-Dec;163:14-21. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2024.04.004. Epub 2024 Apr 24. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 38664120 Review.
-
The roles of gene duplications in the dynamics of evolutionary conflicts.Proc Biol Sci. 2024 Jun;291(2024):20240555. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2024.0555. Epub 2024 Jun 12. Proc Biol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38865605 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Meiotic drive impacts expression and evolution of x-linked genes in stalk-eyed flies.PLoS Genet. 2014 May 15;10(5):e1004362. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004362. eCollection 2014. PLoS Genet. 2014. PMID: 24832132 Free PMC article.
-
Sex chromosome drive.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2014 Dec 18;7(2):a017616. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a017616. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2014. PMID: 25524548 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Andersen C. L., Jensen J. L., Orntoft T. F., 2004. Normalization of real-time quantitative reverse transcription-PCR data: a model-based variance estimation approach to identify genes suited for normalization, applied to bladder and colon cancer data sets. Cancer Res. 64: 5245–5250 - PubMed
-
- Atlan A., Capillon C., Derome N., Couvet D., Montchamp-Moreau C., 2003. The evolution of autosomal suppressors of sex-ratio drive in Drosophila simulans. Genetica 117: 47–58 - PubMed
-
- Atlan A., Joly D., Capillon C., Montchamp-Moreau C., 2004. Sex-ratio distorter of Drosophila simulans reduces male productivity and sperm competition ability. J. Evol. Biol. 17: 744–751 - PubMed
-
- Atlan A., Mercot H., Landre C., Montchamp-Moreau C., 1997. The sex-ratio trait in Drosophila simulans: geographical distribution if distortion and resistance. Evolution 51: 1886–1895 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
