Oocyte maturity in repeated ovarian stimulation
- PMID: 22384448
- PMCID: PMC3283078
- DOI: 10.5653/cerm.2011.38.4.234
Oocyte maturity in repeated ovarian stimulation
Abstract
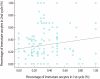
Objective: During stimulated IVF cycles, up to 15% of oocytes are recovered as immature. The purpose of this study was to investigate the trend of oocyte maturity in repeated ovarian stimulation for IVF.
Methods: One hundred forty-eight patients were selected who underwent two consecutive IVF cycles using same stimulation protocol during 2008 to 2010. Ovarian stimulation was performed with FSH and human menopausal gonadotropin and flexible GnRH antagonist protocol in both cycles. Oocyte maturity was assessed according to presence of germinal vesicle (GV) and the first polar body. Immature oocyte was defined as GV stage or metaphase I oocyte (GV breakdown with no visible polar body) and cultured up to 48 hours. If matured, they were fertilized with ICSI.
Results: Percentages of immature oocytes were 30.8% and 32.9% (p=0.466) and IVM rates of immature oocytes were 36.2% and 25.7% (p=0.077), respectively. A significant correlation was noted between percentage of immature oocytes in the two cycles (R=0.178, p=0.03). Women with >40% immaturity in both cycles (n=21) showed lower fertilization rate of in vivo matured oocytes (56.4% vs. 72.0%, p=0.005) and lower pregnancy rate (19.0% vs. 27.1%, p=0.454) after the second cycle when compared with women with <40% immaturity (n=70). In both groups, female age, number of total retrieved oocyte and embryos transferred were similar.
Conclusion: In repeated ovarian stimulation cycles for IVF, the immature oocyte tended to be retrieved repetitively in consecutive IVF cycles.
Keywords: Human; In vitro maturation; Oocyte maturity; Repeated ovarian stimulation.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
References
-
- Dekel N, Sherizly I, Phillips DM, Nimrod A, Zilberstein M, Naor Z. Characterization of the maturational changes induced by a GnRH analogue in the rat ovarian follicle. J Reprod Fertil. 1985;75:461–466. - PubMed
-
- Seibel MM, Smith DM, Levesque L, Borten M, Taymor ML. The temporal relationship between the luteinizing hormone surge and human oocyte maturation. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1982;142:568–572. - PubMed
-
- Testart J, Frydman R, Feinstein MC, Thebault A, Roger M, Scholler R. Interpretation of plasma luteinizing hormone assay for the collection of mature oocytes from women: definition of a luteinizing hormone surge-initiating rise. Fertil Steril. 1981;36:50–54. - PubMed
-
- De Vos A, Van de Velde H, Joris H, Van Steirteghem A. In-vitro matured metaphase-I oocytes have a lower fertilization rate but similar embryo quality as mature metaphase-II oocytes after intracytoplasmic sperm injection. Hum Reprod. 1999;14:1859–1863. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources