Evaluation of the Steelex M600H coagulometer prothrombin time-international normalized ratio assay with Steelex test reagents
- PMID: 22384527
- PMCID: PMC4062317
- DOI: 10.11613/bm.2012.014
Evaluation of the Steelex M600H coagulometer prothrombin time-international normalized ratio assay with Steelex test reagents
Abstract
Introduction: The aim of the present study was to validate prothrombin time (PT) international normalized ratio (INR) results obtained using Steelex test reagents and a Steelex coagulometer (Steelex Scientific Instrument Company, Beijing, China), in comparison with use of a well-established standard test employing Pacific Hemostasis reagents (Fisher Diagnostics, Middletown, VA, USA) and Teco Coatron A4 coagulometer (Teco Medical Instruments GmbH, Neufahrn, Germany).
Materials and methods: Between- and within-day coefficients of variation (CVs) of both assays were calculated using control samples provided by the test manufacturers. Samples from 90 subjects were collected and INR values were determined in a double-blind parallel manner employing both systems.
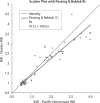
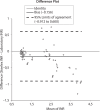
Results: The within-day coefficients of variation (CVs) in INR estimates ranged from 2.6% (INR = 1.12) to 3.1% (INR = 2.51) for the Steelex system and from 2.1% (INR = 1.09) to 1.8% (INR = 2.8) for the Pacific test; the between-day values ran from 3.4% (INR = 1.16) to 7.9% (INR = 2.64) and from 3.3% (INR = 1.1) to 2.3% (INR = 2.7), respectively. Passing-Bablok fit of the of the Steelex and Pacific methods yielded the equation: Steelex INR = 0.85 (0.79-0.91) x Pacific INR + 0.12 (-0.02-0.21), whereas the CUSUM linearity P value was < 0.01. The mean bias as determined by the Bland-Altman test was -0.156 (-0.912-0.600).
Conclusion: The results obtained using Steelex reagents and the M600H coagulometer are not equivalent to those obtained using Pacific Hemostasis reagents and a Teco Coatron A4 coagulometer, at least in the therapeutic range.
Uvod:: Cilj ovog istraživanja je validirati rezultate određivanja protrombinskog vremena (PV) međunarodnim normaliziranim omjerom (engl. international normalized ratio, INR) dobivene reagensima tvrtke Steelex na njihovom koagulometru (Steelex Scientific Instrument Company, Peking, Kina) u usporedbi s često primjenjivanim standardnim testom tvrtke Pacific Hemostasis (Fisher Diagnostics, Middletown, Virginia, SAD) na koagulometru proizvođača Teco Coatron A4 (Teco Medical Instruments GmbH, Neufahrn, Njemačka).
Materijali i metode:: Za oba su testa izračunati koeficijenti varijacije (CV) iz dana u dan i u seriji primjenjujući kontrolne uzorke od proizvođača testa. Sakupljeni su uzorci od 90 ispitanika te su im određene INR vrijednosti dvostruko slijepim određivanjem primjenjujući oba sustava.
Rezultati:: Koeficijenti varijacije u seriji (CV) kod određivanja INR varirali su kod Steelexovog sustava od 2,6% (INR = 1,12) do 3,1% (INR = 2,51) i kod testa tvrtke Pacific od 2,1% (INR = 1,09) do 1,8% (INR = 2,8); vrijednosti iz dana u dan su za Steelexov sustav sezale od 3,4% (INR = 1,16) to 7,9% (INR = 2,64) a za test tvrtke Pacific od 3,3% (INR = 1,1) do 2,3% (INR = 2,7). Passing Bablokovom regresijom Steelexove metode i metode proizvođača Pacific dobivena je jednadžba: Steelex INR = 0,85 (0,79–0,91) × Pacific INR + 0,12 (−0,02–0,21), gdje je P vrijednost CUSUM-ovog testa linearnosti bila < 0,01, a srednja sustavna pogrješka određena Bland-Altmanovim testom iznosila je −0,156 jedinica (−0,912-0,600).
Zaključak:: Rezultati dobiveni primjenom Steelexovih reagensa na koagulometru M600H nisu, što se terapeutskog raspona tiče, ekvivalentni rezultatima dobivenim primjenom reagensa tvrtke Pacific Hemostasis na koagulometru Teco Coatron A4.
Figures
References
-
- Jackson CM, Esnouf MP. Has the time arrived to replace the quick prothrombin time test for monitoring oral anticoagulant therapy? Clin Chem. 2005;51:483–5. - PubMed
-
- WHO Expert Committee on Biological Standardisation. Thirty-third Report. Technical Report Series 687. Vol. 81. Geneva: WHO; 1983. - PubMed
-
- International Committee for Standardisation in Haematology International Committee On Thrombosis and Haemostastis. ICSH/ICTH recommendations for reporting prothrombin time in oral anticoagulant control. Thromb Haemost. 1985;53:155. - PubMed
-
- Cunningham MT, Johnson GF, Pennell BJ, Olson JD. The reliability of manufacturer-determined, instrument-specific international sensitivity index values for calculating the international normalized ratio. Am J Clin Pathol. 1994;102:128–33. - PubMed
-
- van Rijn JL, Schmidt NA, Rutten WP. Correction of instrument and reagent based differences in determination of the international normalized ratio (INR) for monitoring anticoagulant therapy. Clin Chem. 1989;35:840–3. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous