Mycobacterium tuberculosis Rv0652 stimulates production of tumour necrosis factor and monocytes chemoattractant protein-1 in macrophages through the Toll-like receptor 4 pathway
- PMID: 22385341
- PMCID: PMC3403266
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2012.03575.x
Mycobacterium tuberculosis Rv0652 stimulates production of tumour necrosis factor and monocytes chemoattractant protein-1 in macrophages through the Toll-like receptor 4 pathway
Abstract
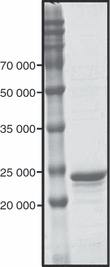
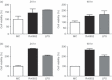
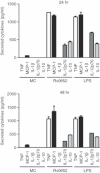
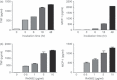
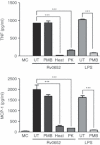
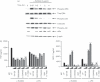
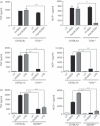
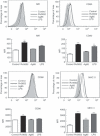
Mycobacterial proteins interact with host macrophages and modulate their functions and cytokine gene expression profile. The protein Rv0652 is abundant in culture filtrates of Mycobacterium tuberculosis K-strain, which belongs to the Beijing family, compared with levels in the H37Rv and CDC1551 strains. Rv0652 induces strong antibody responses in patients with active tuberculosis. We investigated pro-inflammatory cytokine production induced by Rv0652 in murine macrophages and the roles of signalling pathways. In RAW264.7 cells and bone marrow-derived macrophages, recombinant Rv0652 induced predominantly tumour necrosis factor (TNF) and monocyte chemoattractant protein (MCP)-1 production, which was dependent on mitogen-activated protein kinases and nuclear factor-κB. Specific signalling pathway inhibitors revealed that the extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2), p38 and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) pathways were essential for Rv0652-induced TNF production, whereas the ERK1/2 and PI3K pathways, but not the p38 pathway, were critical for MCP-1 production in macrophages. Rv0652-stimulated TNF and MCP-1 secretion by macrophages occurred in a Toll-like receptor 4-dependent and MyD88-dependent manner. In addition, Rv0652 significantly up-regulated the expression of the mannose receptor, CD80, CD86 and MHC class II molecules. These results suggest that Rv0652 can induce a protective immunity against M. tuberculosis through the macrophage activation.
© 2012 The Authors. Immunology © 2012 Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization. Report. Global Tuberculosis Control-Surveillance, Planning, Financing. Geneva, Switzerland: WHO; 2008. WHO/HTM/TB/2008.393.
-
- Colditz GA, Berkey CS, Mosteller F, Brewer TF, Wilson ME, Burdick E, Fineberg HV. Efficacy of BCG vaccine in the prevention of tuberculosis. Meta-analysis of the published literature. JAMA. 1994;271:698–702. - PubMed
-
- Flynn JL, Chan J. Immunology of tuberculosis. Annu Rev Immunol. 2001;19:93–129. - PubMed
-
- Schluger NW, Rom WN. The host immune response to tuberculosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1998;157:679–91. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

