Effects of Hofmeister ions on the α-helical structure of proteins
- PMID: 22385862
- PMCID: PMC3283803
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpj.2012.01.035
Effects of Hofmeister ions on the α-helical structure of proteins
Abstract
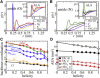
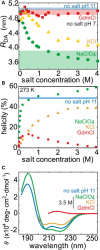
The molecular conformation of proteins is sensitive to the nature of the aqueous environment. In particular, the presence of ions can stabilize or destabilize (denature) protein secondary structure. The underlying mechanisms of these actions are still not fully understood. Here, we combine circular dichroism (CD), single-molecule Förster resonance energy transfer, and atomistic computer simulations to elucidate salt-specific effects on the structure of three peptides with large α-helical propensity. CD indicates a complex ion-specific destabilization of the α-helix that can be rationalized by using a single salt-free computer simulation in combination with the recently introduced scheme of ion-partitioning between nonpolar and polar peptide surfaces. Simulations including salt provide a molecular underpinning of this partitioning concept. Furthermore, our single-molecule Förster resonance energy transfer measurements reveal highly compressed peptide conformations in molar concentrations of NaClO(4) in contrast to strong swelling in the presence of GdmCl. The compacted states observed in the presence of NaClO(4) originate from a tight ion-backbone network that leads to a highly heterogeneous secondary structure distribution and an overall lower α-helical content that would be estimated from CD. Thus, NaClO(4) denatures by inducing a molten globule-like structure that seems completely off-pathway between a fully folded helix and a coil state.
Copyright © 2012 Biophysical Society. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Perchlorate-induced formation of the alpha-helical structure of mastoparan.J Biochem. 1994 Oct;116(4):910-5. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a124615. J Biochem. 1994. PMID: 7883768
-
Design and characterization of the anion-sensitive coiled-coil peptide.Protein Sci. 1997 Jul;6(7):1396-404. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560060703. Protein Sci. 1997. PMID: 9232640 Free PMC article.
-
Sodium perchlorate effects on the helical stability of a mainly alanine peptide.Biophys J. 2010 Jan 20;98(2):186-96. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2009.10.013. Biophys J. 2010. PMID: 20338840 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of amphipathic helical peptide denaturation by guanidinium chloride and urea: a molecular dynamics simulation study.J Comput Aided Mol Des. 2010 Oct;24(10):829-41. doi: 10.1007/s10822-010-9377-x. Epub 2010 Aug 10. J Comput Aided Mol Des. 2010. PMID: 20697778
-
Distinct and Nonadditive Effects of Urea and Guanidinium Chloride on Peptide Solvation.J Phys Chem Lett. 2019 Dec 5;10(23):7406-7413. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.9b03004. Epub 2019 Nov 19. J Phys Chem Lett. 2019. PMID: 31721587
Cited by
-
'Reverse' Hofmeister effects on the sol-gel transition rates for an α-helical peptide-PEG bioconjugate.Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2018 Aug 1;20(30):20287-20295. doi: 10.1039/c8cp03316a. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2018. PMID: 30039819 Free PMC article.
-
Computing on actin bundles network.Sci Rep. 2019 Nov 4;9(1):15887. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-51354-y. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31685834 Free PMC article.
-
Divalent magnesium cation concentrations determine the formation of tofu-like precipitates with differing urea solubilities.Heliyon. 2018 Sep 24;4(9):e00817. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2018.e00817. eCollection 2018 Sep. Heliyon. 2018. PMID: 30259000 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of methods for evaluating structural stability of cell envelope fragments in hypersaline brines as biosignatures of ancient microbial life.Sci Rep. 2025 Aug 6;15(1):28677. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-11211-7. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40770198 Free PMC article.
-
Tyrosine Rotamer States in Beta Amyloid: Signatures of Aggregation and Fibrillation.ACS Omega. 2018 Nov 27;3(11):16046-16056. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.8b02408. eCollection 2018 Nov 30. ACS Omega. 2018. PMID: 31458243 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hofmeister F. Zur Lehre von der wirkung der salze. Zweite Mittheilung. Arch. Exp. Pathol. Pharmakol. 1888;24:247–260.
-
- Von Hippel P.H., Schleich T. Ion effects on solution structure of biological macromolecules. Acc. Chem. Res. 1969;2:257–265.
-
- Nandi P.K., Robinson D.R. The effects of salts on the free energies of nonpolar groups in model peptides. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1972;94:1308–1315. - PubMed
-
- Nandi P.K., Robinson D.R. The effects of salts on the free energy of the peptide group. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1972;94:1299–1308. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

