A delicate interplay of structure, dynamics, and thermodynamics for function: a high pressure NMR study of outer surface protein A
- PMID: 22385863
- PMCID: PMC3283806
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpj.2011.12.010
A delicate interplay of structure, dynamics, and thermodynamics for function: a high pressure NMR study of outer surface protein A
Abstract
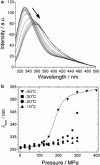
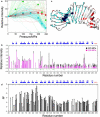
Outer surface protein A (OspA) is a crucial protein in the infection of Borrelia burgdorferi causing Lyme disease. We studied conformational fluctuations of OspA with high-pressure (15)N/(1)H two-dimensional NMR along with high-pressure fluorescence spectroscopy. We found evidence within folded, native OspA for rapid local fluctuations of the polypeptide backbone in the nonglobular single layer β-sheet connecting the N- and C-terminal domains with τ << ms, which may give the two domains certain independence in mobility and thermodynamic stability. Furthermore, we found that folded, native OspA is in equilibrium (τ >> ms) with a minor conformer I, which is almost fully disordered and hydrated for the entire C-terminal part of the polypeptide chain from β8 to the C-terminus. Conformer I is characterized with ΔG(0) = 32 ± 9 kJ/mol and ΔV(0) = -140 ± 40 mL/mol, populating only ∼0.001% at 40°C at 0.1 MPa, pH 5.9. Because in the folded conformer the receptor binding epitope of OspA is buried in the C-terminal domain, its transition into conformer I under in vivo conditions may be critical for the infection of B. burgdorferi. The formation and stability of the peculiar conformer I are apparently supported by a large packing defect or cavity located in the C-terminal domain.
Copyright © 2012 Biophysical Society. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




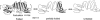
References
-
- Akasaka K., Yamada H. On-line cell high-pressure nuclear magnetic resonance technique: application to protein studies. Methods Enzymol. 2001;338:134–158. - PubMed
-
- Akasaka K. Probing conformational fluctuation of proteins by pressure perturbation. Chem. Rev. 2006;106:1814–1835. - PubMed
-
- Kitahara R., Sareth S., Akasaka K. High pressure NMR reveals active-site hinge motion of folate-bound Escherichia coli dihydrofolate reductase. Biochemistry. 2000;39:12789–12795. - PubMed
-
- Kitahara R., Yokoyama S., Akasaka K. NMR snapshots of a fluctuating protein structure: ubiquitin at 30 bar-3 kbar. J. Mol. Biol. 2005;347:277–285. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

