Mechanisms for insulin resistance: common threads and missing links
- PMID: 22385956
- PMCID: PMC3294420
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.02.017
Mechanisms for insulin resistance: common threads and missing links
Abstract
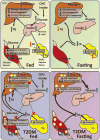
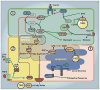
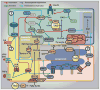
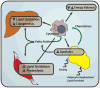
Insulin resistance is a complex metabolic disorder that defies explanation by a single etiological pathway. Accumulation of ectopic lipid metabolites, activation of the unfolded protein response (UPR) pathway, and innate immune pathways have all been implicated in the pathogenesis of insulin resistance. However, these pathways are also closely linked to changes in fatty acid uptake, lipogenesis, and energy expenditure that can impact ectopic lipid deposition. Ultimately, these cellular changes may converge to promote the accumulation of specific lipid metabolites (diacylglycerols and/or ceramides) in liver and skeletal muscle, a common final pathway leading to impaired insulin signaling and insulin resistance.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Aguirre V, Uchida T, Yenush L, Davis R, White MF. The c-Jun NH(2)-terminal kinase promotes insulin resistance during association with insulin receptor substrate-1 and phosphorylation of Ser(307) The Journal of biological chemistry. 2000;275:9047–9054. - PubMed
-
- Anderson CM, Olefsky JM. Phorbol ester-mediated protein kinase C interaction with wild-type and COOH-terminal truncated insulin receptors. J Biol Chem. 1991;266:21760–21764. - PubMed
-
- Arkan MC, Hevener AL, Greten FR, Maeda S, Li ZW, Long JM, Wynshaw-Boris A, Poli G, Olefsky J, Karin M. IKK-beta links inflammation to obesity-induced insulin resistance. Nature medicine. 2005;11:191–198. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

